|
Mid-infrared
lasers: quantum cascade lasers
Quantum cascade lasers
(QCLs) are semiconductor lasers that emit in the mid-infrared to THz
regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. QCLs are unipolar
devices based on intersubband transitions.
QCLs play important roles in various applications such as standoff
chemical detection, photoacoustic sensing,
environmental monitoring, medical diagnosis, etc.
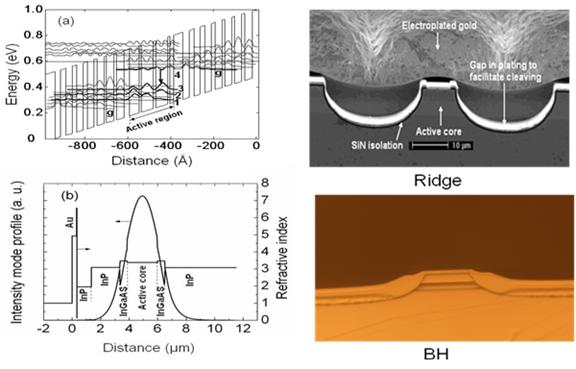
QCL energy band structures, mode
profile, BH waveguide, ridge waveguide.
 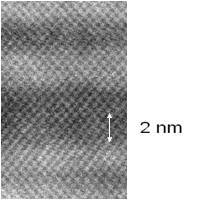
Atomic layers inside a QCL that consists of hundreds of
layers. Each layer thickness is a few nm.
(1)
Integrated tunable DBR QCL
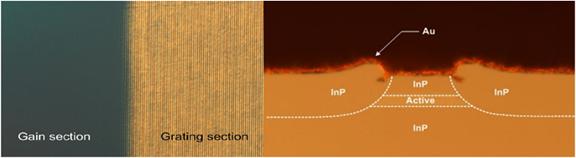
 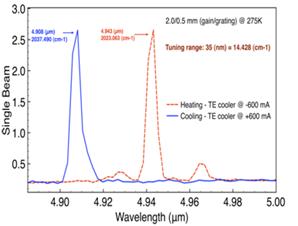
Tunable DBR QCL with two sections. Grating and gain
sections; assembly of DBR QCL; wavelength tuning; cross-section of BH
structure.
Ref:
Liwei Cheng, Dingkai Guo, Xing Chen, Douglas Janssen and Fow-Sen Choa,
“Integrated tunable DBR QCLs”, SPIE Photonic West, paper 7616-44, San
Francisco, CA, Jan. 23-28, 2010.
(2)
Super-structure grating

A super structure grating with variable grating periods
(3)
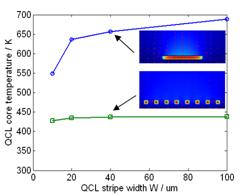
Thermal simulation of QCLs
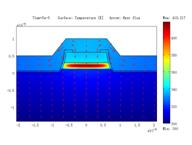 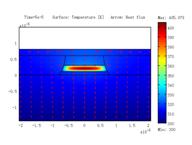 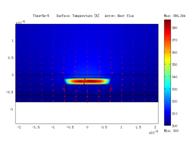
Thermal analysis of QCL with ridge, BH structures, and
BH structure with epi-down bonding
(4)
High power QCL array
 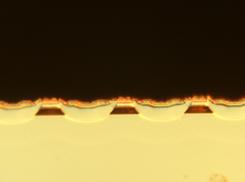
 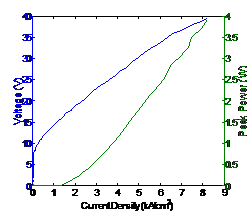
(5)
Surface emitting QCL array
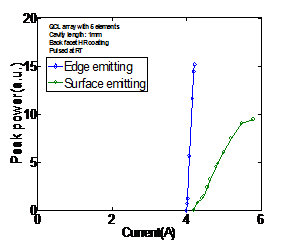 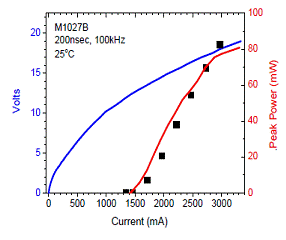
Comparison of edge emitting and surface emitting. Surface
emitting QCL array with 5 emitters, both laser facets HR coated.
Ref:
Xing Chen, Liwei Cheng, Dingkai Guo, Fow-Sen Choa,
"Heat dissipation consideration of high-power mid-infrared
quantum cascade laser arrays," in CLEO: Science and Innovations,
OSA Technical Digest (online) (Optical Society of America, 2012),
paper CTh3N.7.
Xing Chen, Liwei Cheng, Dingkai Guo, Fow-Sen Choa, Jiun-Yun Li, John Bruno, John Bradshaw, Kevin Lascola, Richard Leavitt, John Pham, Fred Towner,
“Surface emitting quantum cascade laser arrays” Frontiers in Optics,
paper FTh4D.8, Oct. 14-18, 2012
|