 Homework 1 is assigned
Homework 1 is assigned
These are not intended to be complete lecture notes. Complicated figures or tables or formulas are included here in case they were not clear or not copied correctly in class. Computer commands, directory names and file names are included. Specific help may be included here yet not presented in class. Source code may be included in line or by a link. Lecture numbers correspond to the syllabus numbering.
Introduction: Hello, my name is Jon Squire and I have been using computers to solve many problems since 1959. I have about 1 million lines of source code, written over the past 50 years. How can that be? Check the numerical computation: 1,000,000/50 years is 20,000 lines per year. 20,000/200 working days per year is 100 lines per working day. With a lot of reuse, cut-and-paste, same programs and data files including scripts for many languages on many operating systems, easy. On a job, 20,000/(50 weeks*5 days per week) is 80 lines per day. 80/8 hours is 10 lines per hour. You can do that. You may not save every line you type. sad. For 25 years I was Software Engineering Manager for the Westinghouse Defense and Space Center, now Northrop Grumman. I was promoted to three levels of management and was still able to develop some of my own software while managing my Budget Center EH3. Now you know something about me, please fill out the survey so I know something about your background. Please turn in survey as you leave. Overview: Things you might not know This section will use a software development "Waterfall Model" Later we cover what another section is using, the "Spiral Model"Homework 1 is assigned
I specifically used "A" because there are many software development processes. Some differences are due to the customer or area: Real Time Operating System End User Commercial Product Mathematical Modeling and Simulation Browser Applications Phone Applications Mission Critical Project etc. Some differences are due to operating system or language or tool kits: Windows, Unix, Linux, MacOSX, etc. C, Java, Python, Fortran, Ada, Html, PHP, SQL, etc. OpenGL, LAPACK, VisualStudio, Eclipse, etc. We will cover a specific development process that you will actually use to develop your term team project. As I have said, commercial team software development is very different from you developing your own software. Thus, we look in detail at your project requirements as a specific development process. CS345 Project
Almost all software producing organizations have some form of software quality assurance. Software Quality Assurance, SQA, consists of a means of monitoring the software engineering processes and methods used to ensure software quality. The means and methods can vary from a small amount of monitoring to almost microscopic observation of every detail in every step of the software development process.. Some Software Quality Assurance Organizations, SQAO, are guided by ensuring conformance to one or more standards, such as ISO 9000 series or CMU developed Capability Maturity Model Integration, CMMI. Some software development requires conformance to specific standards. The SQAO has management, professionals with various expertise, staff, tools, and Software Quality Plan. For the CMSC 345 Project, we will cover and support some of the CMMI. Management has a standard statement: "If you can not measure it, you can not manage it." An example of a tool my section wrote, for computing cyclomatic complexity, the testing aspects to be covered later, is STEST. stest.shtml Our Software Quality Assurance Organization has the following task, for which they must keep records: A new project is started, record its name and date and any other available information. The System Requirements Specification, SRS, must be reviewed and the date of the review recorded. There may be corrections required, these must be recorded and the final SQA approval date recorded. SQA keeps a copy of all documents and checks previous documents for possible change when additional documents are reviewed. The System Design Document, SDD, must be reviewed and the date recorded. There may be corrections required, these must be recorded and the final SQA approval date recorded. Rapid prototypes are shown to SQA, yet not kept by SQA. The User Interface Design Document, UI, must be reviewed and the date recorded. There may be corrections required and these must be recorded and the final SQA approval date recorded. At any time, any level of management may want a summary of the projects SQA approvals and dates. Now code is being produced that will be submitted as it is coded, to the SQA approved configuration tool. e.g. SVN, CVS, etc. covered in lecture 7. Code Inspections are performed and some are by just the development team, some may have a SQA person attend the review, the final review prior to commit may be conducted and recorded by SQA. There may be a style guide required by SQA and checked by SQA. Style guides are covered in lecture 4. The development team submits the Code Inspection Report Document, CIR, to SQA for approval. The approval date and possible corrective action are recorded. There may be quality defects that are counted and recorded. Final testing of the product will be performed by the development team and when they are satisfied, SQA will witness the test procedure and possibly require additional tests. Defects are counted and recorded. The Testing Report Document, TR, is submitted for review and the date recorded. As a part of the testing process, SQA may have required metrics that must be measured. Software Metrics are covered in lecture 5. The product installation and use manual, Administrator Manual, AM, is submitted to SQA for review and the date of final approval is recorded. The product may now be delivered to customers. A competitive product may require benchmarks. There may be a "ticket" system for customers to submit defect reports. This would be maintained by SQA in order to gather defect statistics. Acknowledged problems go to the part of the team that will do the software maintenance. The Software Quality Assurance Organization will provide quality and time data to the marketing and proposal organizations when when they are bidding new projects. More information on the companies organization chart will be covered later.
First: Brandt Braunschweig brandtb1@umbc.edu has an opertunity for you. #include "style_guide.shtml" Homework 2 is assigned
Management class says: "If you can not measure it, you can not manage it."KSLOC and NBNC
There are many metrics that software management needs in order to do their job. A primary metric is used to determine a profitable bid price for a new project. Managers and their company tend to keep a record of previous projects including labor hours and cost. For software the most primitive metric is size, in terms of KSLOC, kilo source lines of code. Most software products that are sold by a company are kept in a software configuration management, CM, repository. This is both for the potential reuse of the software and for use in predicting cost and quality. The software quality assurance organization is responsible for: a) measuring software quality b) improving software quality c) predicting software quality It happens that measuring total lines of code can be very easy. You as a student can easily count the number of lines of code you have in your GL account. For example, you have java code: In a command window, in your login directory, type: wc -l `find . -name \*.java` # watch back ticks, gives number of lines wc -l `find . -name \*.py` # number of lines of Python, etc. There can be a large variation in number of lines for various individuals. When I was estimating, I used NBNC lines. A computer program easily counted non-comment non-blank lines. I had programs for several languages that my group produced. What may be a surprising data point, for embedded software for Department of Defense, I estimated one labor hour per NBNC line of code. I estimated the NBNC lines of code based on previous completed contracts. This estimate included documents, meetings, writing and testing code, presentations. When it came to just writing code, I had people who could do 20 lines per hour. Keep this a secret between us!Types of software complexity measures
Over the years many metrics have been proposed and used in various ways. McCabe Cyclomatic Complexity and Halstead Software Metrics are covered below. Function Points and other metrics may be used by the company where you work. An example, one data point, of software quality vs. development methodology, based on function points is: This was from an article that did not completely define the details of the measurement, yet shows a trend. The Carnegie Mellon University, CMU, Software Engineering Institute, SEI, designed a Capability Maturity Model, CMM, that a software organization may use to determine their level of maturity, from lowest 1, to highest 5. CMU SEI CMM Level 1: 0.75 defect rate per function point CMU SEI CMM Level 2: 0.44 CMU SEI CMM Level 3: 0.27 CMU SEI CMM Level 4: 0.14 CMU SEI CMM Level 5: 0.05Halstead Complexity Measure
First, define four types to be counted in source code: n1 - the number of distinct operators types e.g. = + - [ ( ++ n2 - the number of distinct operands, variable names, function names, ... N1 - the total number of operators N2 - the total number of operands Note that style in the C language can give different values i++; N1 = 1 N2 = 1 typically do not count ";" in C language i += 1; N1 = 1 N2 = 2 each unique constant is an operand i = i + 1; N1 = 2 N2 = 3 which is more error prone? might count [ and ] or just count [, same for ( ) and { } typically do not count data declaration type statements or /* */ counting can vary with language, may count 2 for each : in Python Then Halstead measures n = n1 + n2 program vocabulary N = N1 + N2 program length, indication of size L = n1*log2(n1) + n2*log2(n2) calculated length V = N log2 n program volume D = n1/2 * N2/n2 difficulty E = D * V effort Some empirical examples T = E/18 seconds coding time (not total project time) B = (E^2/3)/3000 or = V/3000 bugs that we call defects If you would base your project estimate on the above, I have this money making Bridge to sell you. :)McCabe Cyclomatic Complexity
In simple terms, count the number of paths in the control flow graph. In actual terms: Define a block of code as having one entrance and one exit. This would be a path in a control flow graph. An "if" statement in most languages, starts two paths. A "for" statement in most languages, starts two paths, one through the body and one around the body to the end. "break" or "continue" not part of an "if" statement starts two paths. A "case" statement starts as many paths as cases, plus 1 if there is no "other" or "default" part. A "try" statement starts two paths with the exception handler being one of the two paths. Typically require "structured programming" and thus do not allow "go to" or statement labels. My SQA organization used a rule, add 10 to the complexity measure for each "go to". The cyclomatic complexity directly relates to software testing. One part of a quality test is that every path, every block, must be executed at least once. This is, of course, not the only test requirement. The program STEST automated the detection that this test requirement was satisfied. Thus, you can see that a slightly different tool, program, would be needed for each programming language a software organization would produce. Big questions remain, do we include the metrics from libraries we use? What if our organization wrote the library? This could be very language dependent. Do you trust the C math.h and the C++ STL libraries?Other things to count
From history: "Job Control Language", JCL, the name for commands to the operating system to compile, link, attach libraries, etc. needed to make a complete program. This was the name for IBM main-frame computers On VAX VMS, a .com file, On Windows a .bat file, on Unix or Linux, a Makefile, or commands to Eclipse or other development environment. Some organizations may count JCL lines in the total line count. Other options are to count only executable lines or count only executable statements. Another option is to count data definition statements. A simple example is to just count semicolons in C language, this, of course, will not work in Fortran or Python. Thus, a tool is needed for every language an organization uses. Now, you need to be working on the first draft of the Software Requirements Specification, SRS, document. srsTemplate.doc srsTemplate.docx srsA.docx You may copy the file on linux.gl.umbc.edu using the command cp /afs/umbc.edu/users/s/q/squire/pub/download/srsTemplate.doc . (Note "." spoken as "dot", means "here")
There are many types of software testing
Black Box testing: Treat the software as a "black box". Supply inputs, check outputs. Test every item in the requirements specification. White Box testing: You have access to the source code. To get 100% path coverage, you will probably need automation. See "STEST" below. Additional test may be needed to be sure every data structure is used in all the ways they may be used. Unit Testing: Test ever file as it is coded. A) Test as expected in normal use B) Stress test with bad input and overloaded input. C) Exercise every path and data structure D) Expect one or more errors during integration Integration Testing: When doing a bottom up build, not the best development method, combine existing files that call or are called by the new file, module, sub system. When doing top down build, integrate each file, module, subsystem as it is available. Do not trust that Unit Testing has all the defects removed. System Testing: Provide real world data in a simulated environment that would be expected when in production use. Rerun previous tests that are still applicable. Acceptance Testing: Software Quality Assurance review of test procedures and test report. You may have a customer who has been involved. Possibly release a Alpha Test version. Possible release a Beta Test version. Automation helps reduce testing cost and improves reliability. #include "stest.shtml"
You may be able to survive without software configuration management if you are the only person working on a one time project, yet any team project may have a critical need for software configuration management, SCM or CM. A major part of automating configuration management is the version control tool. The remaining part is the management edict to use the tool! Available on all UMBC servers, including Linux.gl.umbc.edu. svn - Subversion cvs - Concurrent Versions System" git - git on GL There are many version control tools in addition to SVN and CVS, such as RCS, SCCS, GIT, etc. Many allow web based access if you have a web place to put the repository. SVN is open source software and can run on just about every operating system. SVN has a section on what equivalent CVS commands would be. CVS is designed for Unix, Linux, MacOSX operating systems with gnu software installed. CVS calls SVN a simpler version control system. Not as flexible. We will look at both and you may or may not want to use one for your team. SVN Subversion CVS Concurrent Versions System" If you are using a software development environment such as Eclipse or NetBeans, it may have a way to connect to a version control system.
The SEI Capability Maturity Model Integration is a process improvement and certification program and service that a software development organization may need or may be required to certify at a specific level.While I was a software engineering manager at the Westinghouse Defense and Space Center, we were required to get level 3 SEI CMMI certification in order to bid on some DoD jobs. As shown below this required us to define our software development process and have a software quality assurance organization to document that we were following the written process. The CMMI was developed by a group of experts from industry, government, and the Software Engineering Institute, SEI, at Carnegie Mellon University, CMU. The maturity level certification was based on having a managed, measurable process with the capabilities in the following levels. An inspection team would come and conduct interviews, observations, records inspection, and would either certify the organization for a specific level, or provide a list of deficiencies. For software development:
Maturity Level 2 - named Repeatable
Configuration Management on all software products Measurement and Analysis of the development process Project Monitoring and Control Project Planning with required documents Process and Product Quality Assurance Requirements Management with required documents Supplier Agreement Management of any subcontracted modulesMaturity Level 3 - named Defined
Decision Analysis and Resolution of process problems Integrated Project Management Organizational Process Definition more than just on a project Organizational process Focus involvement of higher management organizational Training in the software development process Product Integration using the process as a normal way of working Requirements Development for every project Risk Management having backup plans Technical Solution rather than hiding problems Validation part of V and V, checking specifications for correctness Verification that the product meets the specificationsMaturity Level 4 - named Quantitatively Managed
Organizational Process Performance measured and recorded Quantitative Project Management monitored measured and recordedMaturity Level 5 - named Optimizing
Causal Analysis and Resolution observing and improving the process Organizational Performance Management having many levels of management knowledgeable about the process and supporting process improvement. Additional list of requirements, with much overlap, are specified for "services" and "acquisition". Thus, "trickle down requirements"! Upper management support is needed and working level professional cooperation is needed to achieve level 3 and above. A formal quality assurance organization is required and must be funded by projects or overhead or a combination of both. The objective is to have the cost of implementing the formal process be mitigated by not having high cost disasters from failed projects and better company reputation by delivering better quality products. The data on failed software development projects is frightening. One study published the results that are: With data like this from one study, commercial software products: 32% were successful 44% had problems 24% failed completely gets managements interest. management support, companies organization chart SEI CMMI is not the only game in town.ISO 9000 series of standards
The International Standards Organization, ISO, has standards and certifications related to software process. There may be multiple standards organizations, sometimes you may see ISO, IEC. International Electrotechnical Commission. ISO, ANSI. American National Standards Institute. Many programming language standards are ISO, ANSI standards. www.open-std.org/jtc1/sc22/wg14/www/standards C jtc1 ISO Joint Technical Committee One wg14 Working Group 14 There is a working group for every language The standard is the published standard including approved corrigendums e.g. C language standard vs. Kernighan and Ritchie vs. gcc vs. M$. jtc1 sc22 wg5 Fortran jtc1 sc22 wg9 Ada +-----------------------+ More Sayings and Signs in Lecture 26 | The Software Industry | | Is The Problem | +-----------------------+ The System Requirements Specification, SRS is assigned CS345 Project Page Your team needs to set up a way to produce this and the following five documents. The initial templates are in Microsoft Word format. The way you are going to store and update your documents may be used in your SRS. Plan on how defects will be reported, recording user, date, time, document. This may be used in your SRS. The SRS will specify an administrator who can set op projects and assign users to projects. Users may update only documents on the project to which they are assigned. All activities must be recorded so the project report, when asked for, will show a history of the project activities. Basically, plan how you are going to do the project, then you may use that plan or a different plan in the SRS. You may later submit revisions to the SRS as you work the project. Revised 12/15/13
More Development Models, Processes
Barry Boehm Spiral Model
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spiral_modelIBM Rational Unified Model, RUP
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IBM_Rational_Unified_ProcessAgile Software Development Process
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Agile_software_developmentUnified Modeling Language
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unified_Modeling_Language Now do Homework 3
This lecture is presented from an engineers point of view. Lawyers have their own language and logic, quite different from specialized technical people. Always consult a lawyer on any legal matter. "FREE as in free to use and modify, not FREE as in free beer."Be Legal
Do not steal from your competitors Do not hack your competitors computers Do not use illegal wiretap on your competitors Do not violate license or contract termsCompete aggressively
Do get and use competitors pricing Do get and use competitors warranty Do get and use competitors Better Business Bureau rating Do get and use testimonials bashing your competitors Do listen to your competitors in public places e.g. restaurants, bars, airplanes, stores Do copy competitors features that help your salesCategories of Software
Company proprietary software. Commercial licensed software. Open source software.Software Protections
Copyright and Patent. #include "cs345_patent.shtml" License: commercial. open source, Free Software Foundation. GNU General Public License, GPL open source, Berkeley Software Distribution. BSD ComparisonSoftware Cost
1. Initial Cost Some commercial software is available for a trial period free. Some commercial software is free for a somewhat limited version. Some commercial software is free but not open source. Some open source software is free. Some open source software is free with an option to buy support. Some open source software must be purchased. 2. Cost of Ownership Training. Updating. Yearly license fees. Efficiency from a computer and people perspective. In preparing this lecture, it is the first time in over 20 years that I have read a software license/agreement, that I click "yes", in order to use the software. Date: Thu, 19 Sep 2013 Subject: How to Choose the Right BI Vendor Business intelligence (BI) is increasingly important but choosing, implementing, and managing a proper BI solution is not always so simple. Choosing the right vendor is critical and that requires some insight on which providers will have the right type of solution for your particular organization. This free Enterprise Business Intelligence Comparison Guide will give you a more complete picture of the entire BI landscape. * Gain a comprehensive understanding of the BI market place * Compare providers based on technologies and specialties * Discover which BI solutions are supported on mobile devices
Management statement: "It is not a customer unless it has both a need and ability to pay enough for us to make a profit."Risk, not software project specific
Key team member in auto accident. Key team member disabled by medical problem.Risk for software projects
Unrealistic schedule. (It may be phony, management psychology.) Cost overrun. The budgeted labor hours are exceeded. (May be to bad budget estimating, changing requirements, more than predicted defects, configuration management problems, general quality problems, inadequate test plans and testing.) Unrealistic requirement among reasonable requirements. (Some, seemingly harmless statement that can be a show stopper.) Language risk, if everything is specified and the language. (A needed library not available for that specific language.) ((In principle, Universal Turing Machine or any common language can code up any possible algorithm.)) Operating system risk, if everything is specified and the OS. (For knowledgeable developers, requiring Windows, Linux, MacOSX is not a problem. Developing entire application on one OS, then trying to port the application to other OS is high risk.) Not enough information to write specific requirements. (This can cause feature bloat, team working a cross purposes, inability to develop a workable test plan. Generally, this is high risk and will be a failed software development project.) Wrong inputs to write specific requirements. (Error or misunderstanding of customer or product use requirements is high risk. If corrected requirements come after design, design effort lost. After test, both deign and test effort lost. After customer gets software, total project investment lost.) Incomplete testing. (Really bad when customer finds more than typical, or expected number of errors.)Risk avoidance
With Waterfall Model, much risk is avoided by rapid prototyping. Spiral Model risk avoidance: Designed to be a "risk-driven" process model. For each project artifact, requirements specification, design document, test plan, coding: the project team must decide how much detail is enough and how many process cycles are needed to minimize overall risk. (This minimizes risk of a defective product, thus good quality, yet has cost and schedule risk.) Rational Unified Model risk avoidance: Develop iteratively with risk as the primary iteration driver. Manage requirements, only make required changes. Continuously verify quality, use metrics and full SQA activity. Develop and test component by component. Determine credibility of cost and schedule estimates, priorities, and risk. (This model came about based on best practices to develop good quality software. Part of the process is to set realistic cost and schedule requirements.) Agile Model risk avoidance: Each iteration has all functions: requirements analysis, design, coding, unit testing, acceptance testing. This minimizes risk and allows the project to adapt to changes quickly. (The biggest risk, with high probability, is schedule and cost overrun.) Philosophy on personal risk: Statistically, you will be hurt about 90% of the time by a friend or family member or associate. Statistically, you will be hurt about 10% of the time by an enemy or stranger or casual acquaintance. You probably have few enemies and there are more than seven billion strangers you will never encounter. Hurt includes: hurt feelings, loss of money or opportunity, ... An old proverb: "Keep your friends close and your enemies even closer." "Do not believe anything you read or hear." Until you have checked and double checked. Do not repeat anything you read or hear, until you have triple checked independent sources. You do not want to be a liar.Now evaluate your risk
In this course. In your other courses. Any risk avoidance you can do?
Each team will have a laptop or use the instructors laptop to connect to the projector. Teams go in the order of their team number. Introduce your team: Company name Product name Team members Bring up your SRS, point out some parts. Your choice, what you like, what you think is good, etc. About 5 minutes, maximum of 10 minutes. Now the System Design Document, SDD is assigned. CS345 Project
"Simply elegant vs elegantly simple" We will cover methods and techniques for: System Architecture Design System Decomposition Procedural Design Data Structure Design Object-oriented Design Designing to meet requirements Designing to minimize risks Methods of documenting a designSystem Architecture Design
The Architecture includes making the requirements specific about: 1) On what operating systems must the product run. 2) The user interface style: command line or graphical user interface (point and click), some combination based on the actor. 3) The implementation, if not command line, terminal based or web based or other. 4) The language(s) that will be used 5) The tool kits or libraries or data bases that will be used. From specific choices of 1) through 5) a top level single box, with a name, with requirements wording of input and output.System Decomposition
Now the requirements may be designed using multiple boxes for some requirements, one box for some requirements, several requirements in one box. Each box get a specific name that will be traceable through coding and testing. This may be one or mode diagrams with indication of how they fit into the top level architecture box.Procedural Design
For each decomposition box, the control flow may need to be specified. Options include flow diagrams, pseudo code, or other representations. The goal is to have a design without having code and yet not just the requirement. The traditional flow diagram. Well, this example also has some data structure definition.
Data Structure Design
Only having the procedural definition has been shown to be insufficient to express an unambiguous design. The data structures may be presented as tables, or possibly, actual code. The design document will have the full description of data structures with name, type, and possibly where each data item comes from and where, or by what, each data item is used. Some of this may make its way into comments in the code, but do not count on this. From a syntax view a_routine(data_object) An example of plain C, red-black-trees tree_rb.c tree_rb_c.outObject-oriented Design
The Object Oriented includes the Procedural and Data Structure Designs encapsulated where the procedural just operates on the specified data structures. From a syntax view data_object.a_method() An example of Java, different red-black-trees RedBlack.java RedBlack_java.outDesigning to meet requirements
This will typically be a top down design. The first step is to go through all requirements and determine the necessary architecture.Designing to minimize risks
Rapid prototyping of small parts is important. This shows your team can implement what your team is designing. I suggest, for this course, you do not use a new language or library, etc. that no one on your team has used previously.Methods of documenting a design
All of the above. Diagrams, text, tables. See SDD.doc for your next document
The mid term exam covers:
Lectures 1 through 13
Homework 1, 2, 3
30 Multiple choice questions
Software development process has a number of models, processes:
(Each have many variations, small summary below:)
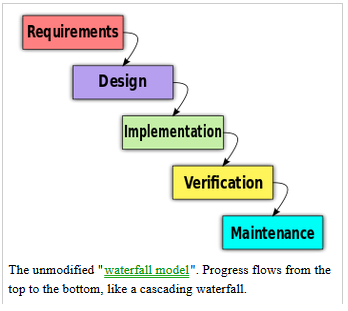
Waterfall Model
Requirements, Design, Implementation, Verification, Maintenance
Scheduled and budgeted development
Risk reduction by rapid prototyping
Spiral Model
Define artifacts concurrently, not a sequence of waterfalls
Each cycle consider stakeholders, evaluate alternatives,
resolve risks, obtain approval.
Risk determines the level of effort, cost
Risk determines the degree of detail, labor effort
Milestones life cycle objectives, architecture, operation
Focus on long term system
Rational Unified Process
Inception phase plan cost, budgets, schedule, requirements
Elaboration phase use-case, architecture, business, prototypes
Construction phase build with possible iterations
Transition phase into production for end users, training
Agile Software Development
Value individuals and interactions, working software,
customer collaboration, respond to change
Self organizing teams, customer satisfaction,
welcome changing requirements, sustainable development
Short iterations with testing
There are a huge number of programming languages that may be used.
From the early days of Fortran, Lisp, Cobol, Algol (all still in use)
came Basic, C, Pascal, Ada, Haskell, Python, Ruby, Java and
many others. Using a language new to the development team members
will increase risk.
The choice of operating system may depend on the platform:
Desktops have over 95% Microsoft Windows
Super Computers have over 95% Linux
Cell Phones have over 75% Android
Tablets have over 45% iOS
Servers have over 40% Linux
Most browsers are W3C compliant
There are many metrics that can be applied to software:
McCabe Cyclomatic Complexity measures branching
Halstead counts unique and total operators and operands
Code size can be counted as lines, KSLOC, or non blank,
non comment lines NBNC.
There are many more, and the practical use is to automate
the measurements and keep records of many projects to
predict cost and schedule.
Style Guides
If source code is delivered to a customer, then having
a style guide for all software in the project is
beneficial and indicates a professional development.
Having every software engineer do initial coding to
a style guide increases cost and have little effect
on quality.
Automating the style guide and processing all software
prior to delivery is most economical.
Software version control is important for team development
There are many version control systems including
CVS, svn, Git, etc. Reduce risk by having a version
control system administrator with prior experience
on a specific system. Most systems are easy to learn
by the users.
Most software development processes have a required set of documents
Various documents may have paragraphs of text, tables, figures,
and defined forms such as use cases, procedural diagrams,
data definitions, architecture diagrams, unified modeling
language, screen shots of user interface, and more.
The Software Quality Assurance organization monitors the
software development
Collecting and reviewing documents SRS, SDD, UI, CIR, TR, AM.
Specifying and checking style guide, metrics, defect reports.
Checking quality of tests at unit, integration, system and
acceptance levels
Providing status reports to management.
Software process certification can be from many organizations
CMU SEI CMMI certifies at initial, managed, defined,
quantitatively managed and optimization levels
ISO 9000 has a larger set of certifications
Professional behavior
Protect your organizations information, company proprietary,
company confidential, for internal use only, and similar markings
Software may be copyrighted and/or patented. Both expose the
content to other organizations, that may be searching various
publicly available data
Open source software may be used by commercial software
developers as long as restrictions, "copyleft", is observed.
Read the instructions first, especially on an exam:
Print your name
Multiple choice, circle the letter that is your answer.
Choose closest if not exact.
Answer all questions with exactly one choice.
(zero, two or more is automatically wrong)
Answer questions in the context of this course.
Comments are ignored. Work very carefully!
See Lecture 14 review, for study guide
Desktop: opengl, Java, Python web: HTML5, javascript Menus, text boxes, selection lists and these are just a few examples Simple html text entry and selection box. form.html form.html as .txt Java menuesW4frame.java Python tk menues (Linux) w4tk.py C with OpenGL menues w4gl.c Now the User Interface Document, UID is assigned. CS345 Project
Each team will have a laptop or use the instructors laptop to connect to the projector. Teams go in the order of their team number. Introduce your team: Company name Product name Team members Bring up your SDD, point out some parts. Your choice, what you like, what you think is good, etc. About 5 minutes, maximum of 10 minutes.More User Interface and Presentation
Watch how characters in a two dimensional world move. Note presentation of expanding to three dimensions and then thinking about living in four dimensions. Yes, this is the classic "Flatland" video. The point is: Do not limit your thinking. "Think outside the box." Then, if you had 3D glasses, see the 4D cube in 3D myapplets/HyprCube.html point dimension 0 line dimension 1 move point square dimension 2 move line cube dimension 3 move square 4D cube dimension 4 move cube ...
Much of this from "Software Engineering" by E.J.Braude Ch 2.
"Project Management" consist of managing the production of a
product within given time and funding limits.
e.g. Syllabus dates and your available time for this class.
The project manager has some control over the following:
1. Total cost of the project, mostly labor hours for software.
2. The capabilities of the product, within the requirements.
3. The quality of the product, minimize defects.
4. The duration of the project, within customer requirements
and balancing 1., 2., 3. above.
Project manager controls:
1. Structure of organization, task assignments for
task leaders, designers, implementers, testers, etc.
2. Managerial process, responsibilities to above,
supervision of employees and possibly contractors
3. The Development Process, e.g. Waterfall, Spiral, RUP,
Agile, etc. and tailoring chosen process to product.
4. Schedule, allocation for each task in each development
phase.
Tradeoff Variables: Cost, Functionality, Quality, Schedule.
From Westinghouse Defense Center manager:
"You can produce the product quickly, low cost, good quality,
pick any two."
Thus, the goal of the project manager is to deliver the product
1. Within required schedule, assuming a reasonable schedule.
2. Within budgeted or quoted cost, assuming reasonable.
3. With a quality that is acceptable to the customer(s).
And, making decisions, based on experience, to take only
reasonable risks. Taking zero risks will cause cost and
schedule overrun.
A road map for Project Management (Some flexibility on order)
1. Understanding project content, scope, time frame, applicable standards
Certifications such as CMM or ISO 9000 may be required.
2. Identify development process
methods, tools, languages, OS, GUI, documentation, support
3. Determine organizational structure
Partition project into task elements
4. Identify managerial process
Assign responsibilities for participants
5. Develop schedule
Times at which the work tasks are to be performed
6. Develop staffing plan, qualifications of the team
7. Begin risk management
Implement cost tracking, schedule tracking, progress tracking,
metrics tracking
8. Identify documents to be produced
e.g. SRS, SDD, CIR, TR, AM or users manual (electronic ?)
9. Begin process itself
My bad humor: Just before a new employee starts their
first day working for me, I place a folder on their desk.
The first page list two or three task and a schedule
that shows their first task is already over due.
Methods to attain a required quality level:
1. Inspections
Check documentation standards are followed.
Quality Assurance code walk throughs, code audits,
code metrics measured, check style guide conformance
2. Formal method being used
Check each stage of development and each task for
compliance with the required formal method.
Check on risk reduction applications such as
code reuse from previous projects, rapid prototyping,
prevention of feature growth beyond specification
3. Testing
Unit test for catching bad inputs, for correct output
given legal input, stress test units that may be
critical to keep product running, no unhandled exceptions,
no access outside arrays, no bad references or pointers.
Integration test, incremental build with testing as each
module is added to the product.
Final acceptance test, end to end, including bad inputs
to check quality of diagnostic messages
(A miss spelled word in a diagnostic message is counted
as a defect. Consider running a spell checker on
every file, both code and data.)
4. General Project Control:
May have large project chart for all to see,
planned schedule and cost and quality measures vs.
actual, updated every week.
Project manager may have a confidential version with
annotation about each task and each participant.
Typically, once a year, every employee must be
evaluated by one or more levels of management. Most
managers keep a confidential file on every person
who is working for them.
Some synonyms:
Participant = worker = employee or contractor = team member
Task = work item = portion = job to be performed
Module = file = code or data = part of product
This was just about "Project Management".
Most companies have a matrix organization consisting
of permanent divisions, departments, groups that are
called "Line Management" and there is typically an
organization chart showing the "Line" organization.
Then, as contracts or jobs are bid and won, or a new
product is to be developed, a "Project" is created with
a "Project Manager" and the project manager forms a
project team by drawing on people from various line
management organizations. A large project may have
one or more deputy managers, one or more accountants
who monitor cost (mostly labor hours), specialist in
product design, product implementation, product testing,
documentation, and possibly a dedicated quality assurance
person. The project may get its own physical area and
move people from their line management desk into the
project area. As a worker, you did not eliminate a boss,
you just acquired another boss. :)
The project would be dissolved when completed or if
the project seems to be failing and is terminated.
Workers would return to their line management desk when
their specific project task on the project was completed.
Yes, layoffs may happen if not enough projects are
available or a major project ends with no replacement
in sight.
The "Line Management" organizations may have their
own internal work such as developing infrastructure,
processes, tools, etc.
Make use of automation and test at every step
Much of this from "Software Engineering" by E.J.Braude Ch 5.
"Software Architecture" similar to the architecture of
a building or other product, form follows function.
A clean, well designed, architecture facilitates minimizing
defects, meeting customer requirements, meeting cost and
schedule objectives, and can be extended and reused.
The software development industry has come a long way.
(There is always room for improvement and innovation.)
We no longer have "programmers" who code up a program to
meet some requirement. We have professionals, often
called "Software Engineers" that use a disciplined process
to develop a computer program or total system of software
and data to meet, possibly complex requirements.
A software architecture starts with the big picture of
system requirements then successively refined the
architecture to the point where detailed design can
proceed with low risk.
Some top level architecture alternatives are:
1. Dataflow
Batch sequential
Pipes and filters
2. Independent components
Parallel communicating processes
Client server systems
Event driven systems
3. Virtual machines
Interpreters
Rule based systems
4. Repository
Database
Hypertext systems
Blackboards
Cloud
5. User interface
Graphical as local application or web based
Point and click, drag and drop
Menus, icons, combination
Command line
6. Layered
Combinations of the above
The chosen architecture for a product is typically in
the System Design Document and may use the format
of IEEE Standard 1016.
A snapshot of the 1016 SDD table of contents is:
1. Introduction
1.1 Purpose
1.2 Scope
1.3 Definitions, acronyms, abbreviations
2. References
3. Decomposition description
3.1 Module decomposition
3.1.1 Module 1 description
3.1.2 Module 2 ...
3.2 Concurrent process decomposition
3.2.1 Process 1 description
3.2.2 Process 2 ...
3.3 Data decomposition
3.3.1 Data 1 description
3.3.2 Data 2 ...
4. Dependency description
4.1 Intermodule dependencies
4.2 Interprocess dependencies
4.3 Data dependencies
5. Interface description
5.1 Module interface
5.1.1 Module 1
5.1.2 Module 2 ...
5.2 Process interface
5.2.1 Process 1
5.2.2 Process 2 ...
6. Detailed design
6.1 Module detailed design
6.1.1 Module 1 detail
6.1.2 Module 2 ...
6.2 Data detailed design
6.2.1 Data 1 detail
6.2.2 Data 2 ...
Hmmmm? No 6.3 Process detailed design?
Processes may run concurrently as actual
operating system processes communicating
with messages, or as threads communicating
via the shared address space.
Moving into parallel programming of products, applications,
programs:
A modern computer will have many cores, each core
typically more powerful than a previous desktop
computer. A core runs a sequence of instructions
using an instruction cache, data cache, integer
and floating point arithmetic units. All cores
in a single processor share the RAM storage,
disk drives and input-output.
Multi processor computers are available that
may have a few to hundreds to thousands of processors.
The processors communicate over an interconnect
network, ethernet, infiniband, etc.
The largest super computer has over one million cores.
A process is a program or part of a program that
is scheduled by the operating system. Every process
has its private address space and typically uses
message passing to communicate with other processes.
A thread is an independent sequence of statements,
in a quality system, executed in a core, in a multi core
computer. All threads of any process, share a common
address space and must follow a discipline of
multiple read, single write, of shared data.
Programming languages typically have threads that
are reasonable to use. Multi processors use
tool kits such as Message Passing Interface, MPI,
or others to allow a single application to use
many processors that may have many cores each.
From tialert@ieee.org Tue Aug 27 10:34:05 2013
Subject: The Institute Online:
Did You Know? Edison Coined the Term "Bug"
You might think the phrase "computer bug" began in the 1940s
when programmer Grace Hopper and her colleagues found a dead
moth in a Harvard University computer. However, it was
actually coined much earlier, by Thomas Edison. With
the help of Paul Israel, editor of the Edison Papers,
the IEEE History Center traces the origins of the phrase.
We now use the term "defect" Rather than "bug" in
professional and quality assurance writing.
Each team will have a laptop or use the instructors laptop
to connect to the projector. Teams go in the order of their
team number.
Introduce your team:
Company name
Product name
Team members
Bring up your UID, point out some parts.
Your choice, what you like, what you think is good, etc.
About 5 minutes, maximum of 10 minutes.
Next, fill in the Code Inspection Report, cir, Template.
It is getting a little harder to work as a team.
In some development processes, this would be called
a "Test Plan" with some reporting of actual testing
included.
Section 1.3 Include a "style guide" consisting of appropriate
coding and commenting conventions for your choice of language
and design. Everyone on the team will be reading the code
and checking against what you write. Including me and
probably your customer. Be reasonable.
Section 1.4 "possible defects" are a list of everything that
you will be testing for. Look for any limits or size
restrictions from your SRS, SDD, and UI. You are basically
listing all the items you will be testing.
e.g. User name can not be more than 31 characters.
(use your applications limits)
One item is "Check that code follows the coding and
commenting conventions."
You may use lists and tables.
Looking ahead to the "Test Report" you may want to
number the items in the list. Yes, there is some
redundancy, yet, testing is an important part of
product development.
Then, the application must be written and your inspection
results recorded in section 3.
Now the Code Inspection Report, CIR is assigned.
CS345 Project
When designing software, consider the platform. For Windows, look at Windows 8 for the trend. For Linux there is Gnome and Unity and KUbuntu, etc. For MacOSX use their style. For tablets and phones, use app style. For some environments, think about this: See the Space Station Windows 8, Microsoft Word
Menu bar standards: "File" on the left "Edit" next to "File" "Help" on the right Homework 5 is assigned
The outline in the Testing Report template is a little skimpy. Some suggestions and discussion are covered in class. It was already mentioned, to number the items in the CIR. When citing the SRS, SDD, or UI, they may be given numbers in the TR. There may be significant variation of test suites based on your teams product. Testing Report template
Lessons Learned from a recent Government procurement. This is not the first government or industry software procurement to have problems, and, it will not be the last. You students can help prevent this in the future. The dismal track record of the implementation of large-scale information technology initiatives even in rigorous and focused corporate environments points up their difficulty. Unexpected obstacles arise, deadlines are missed and budgets are overrun. Maximizing the prospect of success requires providing for slack in the schedule and the budget, structuring projects with clear accountabilities and frequent checkpoints, and assigning oversight responsibility to people with extensive information technology experience rather than general managers who have programmatic commitments. Success also requires some trusting but more verifying. A homeowner who hires a general contractor to build an addition, discusses the project and then goes away for six months probably would be unhappy with the result. The same is true for public managers who hire contractors to perform essential tasks but fail to rigorously oversee every step. Another requisite for success is steadiness and realism in the face of difficulty. Once a project gets off track, there is an overwhelming temptation for everyone involved to circle the wagons and promise rapid repair so as to hold critics at bay. Yet the right response to failure is to surface problems as rapidly as possible and to move more deliberately and carefully, not more quickly. In football, the best teams stick to their playbooks even when they fall behind. When one has fallen behind on a project, it is important to mobilize new resources and management but not to overpromise with respect to how soon and how good a fix is possible. One instance of over-optimism will ultimately be forgotten or forgiven. Repeated over-optimism should not and will not be excused. These are old truths that those responsible for implementing ACA should have heeded. Yet fairness requires recognizing the equally important, and in some ways more fundamental, factor behind the problems implementing any government project, there may be many individuals and elected officials against the project. Large-scale information technology projects in the private sector are hard enough without an organized constituency for failure. It is no exaggeration to say that the failure of ACA has been the prophecy and the hope of many of those responsible for funding implementation of the ACA, confirming the appointments of those who will do the job and overseeing the results. They have been eager to seize on any problems and highlight any controversial judgments. All serve to create an environment in which failure becomes the expectation. The formal process should be: 1) Government or company puts out a Request For Proposal, RFP. This document covers the information we provided in our Software Requirements Specification, SRS. 2) Contractors respond to the RFP with a proposal. This document covers the information we provided in our Software Design Document, SDD, plus a detailed schedule, resume of people who will work on the job, detailed cost estimate and total cost. 3) The Government evaluates the competing proposals, it is poor choice of Government to allow a sole source bidder, and selects the proposal that best meets the government needs at the lowest price. Past history of the bidders is taken into account. Bidders that have missed schedules or had cost overruns get those factors added to their proposed numbers for evaluation purposes. 4) The Government selects a proposal, writes a contract, possibly with some changes in their RFP and the proposal. The contractor may accept the contract or negotiate changes in technical, schedule, cost, etc. 5) Upon receiving a signed contract, both parties stay in contact. There may be informal and formal meetings. Formal meetings typically start with a Preliminary Design review, PDR. Then a final Design Review, DR. 6) Then progress reports and possible demonstrations. A formal Test Requirements Review, TRR, takes place. The last meeting would be the formal Acceptance Test, AT, observation and evaluation. 7) Hopefully, product accepted and contractor paid. Along the way, there is talk of changes by both government and contractor. Changes are supposed to be made official be a contract modification that might schedule change and price change. There is typically a fixed limit, in the law, for how much the money can be spent. For today's lesson: March 23, 2010 ACA was signed into law. Good points: Coverage for children with pre-existing conditions Coverage for children under 26 No lifetime limits on coverage No arbitrary cancellations Right to appeal health plan decisions Consumer Assistance Program (included web pages) Small business tax credit Temporary coverage for people with pre-existing conditions Community health centers But, as usual, the law allowed government agencies, not elected officials, to write "regulations" that have the force of laws. e.g. "You could keep your present insurance." Until the regulations added "unless there was any change to the policy after March 23, 2010, and only if your current policy met the new regulation guidelines." As of 2013, about 1,000,000 policies have been canceled. It is common for a new law to take six months or so to have a competitive RFP for contractor supplied services, like web sites, application software, etc. It is considered good efficient government to have a contract signed within a year. Two years is not unusual. Thus the ACA web site contract might have started in March 2012. Now Politics can play a roll in awarding contracts. The most common ploy to avoid competitive bids, is to just delay. Then, when the government can claim the contract is time critical, they can issue a sole-source contract to some company the Politicians want to do the contract. 2013 award for ACA. Thus, just another added to lessons already learned. Homework 6 assigned
Just to give you an idea of where you will be in
a company structure, I present the "Org Chart".
For any given corporation, the official Organization
Chart, may or may not be available to you. Yet,
you will be able to piece together much of it.
This is hypothetical, based on the management training
that stated "Optimal control is when a manager has
five next lower level managers." Rarely is it exactly
five in the real world. Sometimes more, sometimes less.
Then each manager may have a staff, typically at least
a secretary and a financial or budget controller.
mgr staff
president 1 2
/ \ \ \ \
vice 5 10
president
/ \ \ \ \
division 25 50
manager
/ \ \ \ \
department 125 250
manager
/ \ \ \ \
section 625 1,250
manager
/ \ \ \ \
group 3,125 6,250
manager
/ \ \ \ \
professional 15,625
worker bee
you total 27,343
This is called "line" management
because each has a line to their boss
on the organization chart.
But, it is not that simple in most corporations.
Typically there is a second structure called
project management. Each contract or job will have
a project manager. That project manager may have
five managers reporting, some from the line management
structure above. Most of the worker bees will be
from the line management structure above.
Oh! You now may have two bosses. Ha! if it was only
that simple. Any of your boss's boss may give you
tasks or assignments.
Sorry, story not over yet. The secretaries have a
hierarchy, your boss's secretary implicitly
takes direction from your boss's boss's secretary, etc.
Typically your boss's financial person takes direction
from your boss's boss's financial person.
And both those hierarchies can set rules that you
must follow.
I am assuming the corporation sells products.
Thus among the mix is a marketing organization,
that may have marketeers, and proposal managers.
You may be sent off to work on a proposal.
At least two parts of the proposal are the
technical proposal with a mix of real technical
statements and some subtle sales pitch,
and the cost proposal.
Here the plot thickens. At some management level
a "target cost" will be specified.
Then the "bottom up" cost is calculated based
on past history data. They never agree!
Then comes creative accounting and negotiation
to reach a final sell price.
The corporation described here may have a separate
area or even a separate building for proposal
preparation. A proposal team has a deadline,
usually specified by the customer, and may
work many hours of uncompensated time during
proposal preparation.
Oh! And if this is a DoD or other Government
contract, everyone working on the contract
must record the specific time on a specific
part of the contract. It may be required to
the closest 1/10 of an hour.
So, what about those tasks and assignments
you can be given by other people in the
hierarchy? Well, the corporation has an
accounting system with one or more accounts
for each contract, IR&D independent research
and development accounts, administrative
accounts including sick and vacation time.
Then there is the dreaded "non productive"
account that must be charged for hours
you do not have any other charge number.
Every account has a budget assigned.
The financial hierarchy comes down on
you or any level of manager that
exceeds a budget. Oh! more manipulation
to come in at budget on all budgets.
Be careful, some manipulation may be
illegal on Government and CPFF,
cost plus fixed fee contracts.
You, worker bee, are getting paid for the
work you are doing. You probably expect to
get pay raises and promotions. Typically,
each level of manager gets over 10% more
than the managers below.
Suppose, you are average, thus each year you
learn more and can produce more quantity or
quality. There will be an merit increase budget
passed down the hierarchy. Being average
you may get about 7% per year increase.
This will about double you salary every 10 years.
If you are a top performer and the corporation
is doing well, you may get about 10% per year
increase. This will about double you salary
every 7 years.
Your starting salary is important.
Starting at $10,000, $20,000, $40,000, $80,000
per year in 30 years.
Starting at $20,000, $40,000, $80,000, $160,000
per year in 30 years. You may be 55 years old
and expect to double again and retire at 65.
Sorry, some where along the way, the "Peter Principal"
will happen. "Everyone gets promoted to their
level of incompetence" and stays there or is
downgraded, possibly laid off. Called a rift.
Oh! Who gets laid off? Again, based on the overall
profit of the corporation and future business
estimates, a quota of how many must be laid off
comes down the management hierarchy. Sometimes
it is the least productive that go on the list
first, exceptions may be critical skill, potential,
age would be bad and possibly illegal.
Have a nice day.
This is just a small part of understanding
what may happen in a large corporation.
A small business will be completely different.
HR Department
And then, there is the "Human Recourse Department".
These are the people who actually hire and fire you.
For Human Resource Professionals:
Live Webinar on Smarter Email Management
Smarter Email Management will provide attendees with essential
skills that can improve both the message and the management
aspects of working with email.
Areas covered in the session:
The What, Why and How of Email Etiquette:
* How to create notebooks, sections and pages
* How to easily add information, emails, pictures, even audio to notebooks
* Ideas for how to customize with color, order and style
* How to share all or part of a notebook with others
The What, Why and How of Email Management:
* Learn how to get less email
* Know the 5 questions to ask for all incoming email so you can
make a decision on what to do with it
Delete based on sender
Delete based on subject
Delete based on format
When to stop reading and delete
Is it really worth not deleting
* Learn how to set-up a filing system that will allow you to
file and find it faster
* Learn the 3 habits that if practiced will help you become
an email management pro!
Keep mouse positioned on delete button
Keep finger on the delete Key
When in doubt, delete
* It is approaching one hour a day, spent per employee,
reading and responding to Email.
(Obviously the above, edited, came as Email. "spent"="wasted"?)
Now the Testing Report Document, TRD is assigned.
CS345 Project
Benchmark is a general term in business. It generally means measuring and comparing. In software, some skill is needed to do sucessful benchmarking. The best method of measuring a computers performance is to use benchmarks. Some suggestions from my personal experience preparing a benchmark suite and several updates and personal benchmark experience are presented in pdf format. Lecture here, .pdf Smaller time is better, higher clock frequency is better. time = 1 / frequency T = 1/F and F = 1/T 1 nanosecond = 1 / 1 GHz 1 microsecond = 1 / 1 MHz Do not trust your computers clock or the software that reads and processes the time. First: Test the wall clock time against your watch. time_test.c time_test.java time_test.f90 The program displays 0, 5, 10, 15 ... at 0 seconds, 5 seconds, 10 seconds etc.demonstrate time_test if possible
Note the use of <time.h> and 'time()' Beware, midnight is zero seconds. Then 60 sec/min * 60 min/hr * 24 hr/day = 86,400 sec/day Just before midnight is 86,399 seconds. Running a benchmark across midnight may give a negative time. Then: Test CPU time, this should be just the time used by the program that is running. With only this program running, checking against your watch should work. time_cpu.c The program displays 0, 5, 10, 15 ... at 0 seconds, 5 seconds, 10 seconds etc. Note the use of <time.h> and '(double)clock()/(double)CLOCKS_PER_SEC' I have found one machine with the constant CLOCKS_PER_SECOND completely wrong and another machine with a value 64 that should have been 100. A computer used for real time applications could have a value of 1,000,000 or more. What if you are benchmarking a multiprocessor? For example, a two core or quad core, then use both CPU time and wall time to get average processor loading: time_mp2.c for two cores time_mp4.c for quad cores time_mp8.c for two quad cores time_mp12.c for two six cores The output from a two cores is: time_mp2.out for two core Xeon The output from four cores is: time_mp4.out for Mac quad G5 The output from eight cores is: time_mp8_c.out for AMD 12-core The output from twelve cores is: time_mp12_c.out for AMD 12-core Similar tests in Java time_test.java time_cpu.java time_mp4.java for quad cores time_mp8.java for eight cores time_mp4_java.out for quad Xeon G5 time_mp8_java.out for 8 thread Xeon G5 Time_test and threads in Python time_test.py time_cpu.py To measure very short times, a higher quality, double-difference method is needed. The following program measures the time to do a double precision floating point add. This may be a time smaller than 1ns, 10^-9 seconds. A test harness is needed to calibrate the loops and make sure dead code elimination can not be used by the compiler. The the item to be tested is placed in a copy of the test harness to make the measurement. The time of the test harness is the stop minus start time in seconds. The time for the measurement is the stop minus start time in seconds. The difference, thus double difference, between the harness and measurement is the time for the item being measured. Here A = A + B with B not known to be a constant by the compiler, is reasonably expected to be a single instruction to add B to a register. If not, we have timed the full statement. The double difference time must be divided by the total number of iterations from the nested loops to get the time for the computer to execute the item once. An attempt is made to get a very stable time measurement. Doubling the number of iterations should double the time. Summary of double difference t1 saved run test harness t2 saved t3 saved run measurement, test harness with item to be timed t4 saved tdiff = (t4-t3) - (t2-t1) t_item = tdiff / number of iterations check against previous time, if not close, double iterations The source code is: time_fadd.c fadd on P4 2.53GHz fadd on Xeon 2.66GHz Some extra information for students wanting to explore their computer: Windows OS Linux OS
What is in my computer?
start cd /proc control panel cat cpuinfo system device manager processor etc.
What processes are running in my computer?
ctrl-alt-del ps -el process top How do I easily time a program? command prompt time prog < input > output time
prog < input > output time The time available through normal software calls may be updated less than 30 times per second to more than a million times per second. A general rule of thumb is to have the time being measured be 10 seconds or more. This will give a reasonable accurate time measurement on all computers. Just repeat what is being measured if it does not run 10 seconds. Some history about computer time reporting. There were time sharing system where you bought time on the computer by the cpu second. There is the cpu time your program requires that is usually called your process time. There is also operating system cpu time. When there are multiple processes running, the operating system time slices, running each job for a short time, called a quanta. The operating system must manage memory, devices, scheduling and related tasks. In the past we had to keep a very close eye on how cpu time was charged to the users process verses the systems processes and was "dead time" the idle process, charged to either. From a users point of view, the user did not request to be swapped out, thus the user does not want any of the operating system time for stopping and restarting the users process to be charged to the user. Another historic tidbit, some Unix systems would add one microsecond to the time reported on each system request for the time. Never allowing the same time to be reported twice even if the clock had not updated. This was to ensure that all disk file times were unique and thus programs such as 'make' would be reliable. For more recent SPEC benchmarks, many see CPU integer benchmarks,SPECint, floating point benchmarks,SPECfp www.spec.org/cpu2013/Docs/ Some times you just have to buy the top of the line and forget benchmarks.
Credits go to original speaker or writer. Many credits not known thus none given. Management Philosophy "If you can not measure it, you can not manage it." Peter Principle: "Employees tend to rise to their level of incompetence." Murphy's law: "If anything can go wrong it will." "Murphy was an optimist." "That's funny!" "Funny strange or funny ha ha?" "Think outside the box." "Be careful what you wish for, you may get it." Software completion: "When a software engineer says his project is 90% complete, management knows 1/2 of the cost has been spent." "Those who do not study history are bound to repeat it." "What people learn from history, is that people do not learn from history" "Change is inevitable." "Nothing ever changes." "Nothing ventured, nothing gained." "Better to be safe than sorry." The impossible to answer request: "Please quantify your subjective evaluation." "The Devil is in the details." "Injustice anywhere is a threat to justice everywhere." "The Devil made me do it." "No Guts, No Glory." "If it ain't broke, don't try to fix it." "Go with the flow if it will not bother you 10 years from now." "If it is too good to be true, it probably is." "Nothing is forever. Yet, still do some short term planning and some long term planning." "It is dangerous to be right, when the government is wrong." "There is a reason why in New York Harbor we have the Statue of Liberty, not the Statue of Equality" "The further a society drifts from truth, the more it will hate those who speak it." "A truly moral nation enacts policies that encourage personal responsibility and discourage self-destructive behavior by not subsidizing people who live irresponsibly and make poor choices" "When even one American, who has done nothing wrong, is forced by fear to shut his mind and close his mouth, than all Americans are in peril" "Free enterprise has done more to reduce poverty than all the government programs dreamed up by the Politicians." "We must reject this idea that every time a law is broken, society is guilty rather than the lawbreaker. It is time to restore the American precept that each individual is accountable for his actions" "When you want to help people, you tell them the truth. When you want to help yourself, you tell them what they want to hear" "There are a group of people who would like to silence everybody and have everybody "go along to get along", but that's not going to be very helpful for us in the long run. Somebody has to be courageous enough to actually stand up to the bullies" "Do not believe anything you hear or read. (Until you have checked and double checked.) ((Do not repeat anything you hear or read until you have triple checked from multiple independent sources. You do not want to make yourself a liar))" "A preposition is something you should not end as sentence with." "There never has been, nor will there ever be, a rule that is sometime best broken." (Just have a very good reason.) A bit harsh, yet "The only absolute guarantee in life, is ultimate death." "A place for everything and everything in its place." A few more signs posted in offices: +--------------------------------------------------+ | A cluttered desk is a sign of a cluttered mind. | | A clean desk is a sign of an unstable mine. | | The messier the desk, the more genius the owner. | +--------------------------------------------------+ +-----------------------+ | Safety is no accident | +-----------------------+ +----------------------------------+ | Some days you are the bug. | | Some days you are the windshield | +----------------------------------+ +-----------------------+ | The Software Industry | | Is The Problem | +-----------------------+ +----------------+ | It takes money | Found in a counterfeiters lab | to make money | +----------------+ "Fishing used to be good." While many IT professionals have become less concerned with phishing as it seems these attacks only fool naive consumers, a new generation of sophisticated phishing attacks now target businesses. These phish evade traditional antivirus and anti-phishing products. Using targeted information - often gathered from social media sites, they fool even security-savvy employees into divulging sensitive information or visiting websites that infect machines with dangerous malware. joke or motivation Now the Administrators, AM is assigned. CS345 Project
here is current presentation times in this class.
Team 2 Code Retrievers 11:30 moved to later Thursday
Team 3 YoLo Tech 11:55 moved to 6pm
Team 4 NBD^3 12:20 moved to Thursday
The remaining teams present in the next class.
Nominal 15 minute presentation time.
Maximum 25 minute presentation time includes
maximum 5 minutes for questions.
The entire team is to be a part of their project presentation.
Hopefully, the team practiced the presentation.
Start by introducing the team and rolls each team
member worked.
Go through a complete demonstration from initial login,
examining status, examining previously entered data,
then entering new data of each type, administrator features,
and final logout.
Mention each team members name as they do their part(s)
of the presentation.
Mention customer requests and be sure to show.
Hopefully your customer will be present.
Customer has an evaluation form to fill out.
There may be questions from instructor or customer.
Short concise answers are expected.
instructor form
customer form
Team 1 Optimum 11:30 Team 4 NBD^3 11:50 or after Team 1 Team 5 Gold Inc. 12:10 or after Team 4 Team 6 3456Software 12:30 or after Team 5 Team 2 Code retrievers 4:30 Nominal 15 minute presentation time. maximum 20 minutes including up to 5 minutes of questions. The entire team is to be a part of their project presentation. Hopefully, the team practiced the presentation. Start by introducing the team and rolls each team member worked. Go through a complete demonstration from initial login, examining status, examining previously entered data, then entering new data of each type, administrator features, and final logout. Mention each team members name as they do their part(s) of the presentation. Mention customer requests and be sure to show. Hopefully your customer will be present. Customer has an evaluation form to fill out. There may be questions from instructor or customer. Short concise answers are expected. instructor form customer form
Team 1 Optimum 11:30 Team 4 NBD^3 11:50 or after Team 1 Team 5 Gold Inc. 12:10 or after Team 4 Team 6 3456Software 12:30 or after Team 5 Team 2 Code retrievers 4:30 Nominal 15 minute presentation time. maximum 20 minutes including up to 5 minutes of questions. The entire team is to be a part of their project presentation. Hopefully, the team practiced the presentation. Start by introducing the team and rolls each team member worked. Go through a complete demonstration from initial login, examining status, examining previously entered data, then entering new data of each type, administrator features, and final logout. Mention each team members name as they do their part(s) of the presentation. Mention customer requests and be sure to show. Hopefully your customer will be present. Customer has an evaluation form to fill out. There may be questions from instructor or customer. Short concise answers are expected. instructor form customer form
See lecture 29 for study guide.
[CMSC 345] | [Syllabus] | [Lecture Notes] | [Homework] | [Project] | [Notes, all]
"Those who do not study history are bound to repeat it." "What people learn from history, is that people do not learn from history" Read en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_programming_languages If you are interested in the history of your favorite programming language or some other programming language: Optional Reading: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/C_(programming_language) en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fortran Some general, not so great, "History of Programming Languages" Many other "history" links. en.wiki/History_of_programming_languages
Another reading assignment. A few questions on mid term exam, just basic concepts.




I know "Forage" as "reuse" and this became part of the formal development process at least 25 years ago. I know "tinker" as test any software you are about to reuse. I know "Weld" as integrate existing software into a your new application.
Based on Lecture 9, Spiral, Rational Unified, and Agile Models: Make four lists: 1) List items that are in all three: Spiral, RUP, and Agile Models 2) List items that appear only in the Spiral Model 3) List items that appear only in the Rational Unified Model 4) List items that only appear in the Agile Model use key words, keep each item to one short line
For the SDD your team needs to express your design in writing.
Not literally just words, there are typically diagrams and
figures.
This homework is to just define the data structure for a
node in a balanced binary tree. Each node has a display name,
a value, optional internal use data, and links to two nodes
below.
+--------+
| Root |
| value1 |
+--------+
/ \
/ \
/ \
+--------+ +---------+
| NodeA | | Node7 |
| valuea | | valuex |
+--------+ +---------+
/ \
/ \
+-------+ +--------+
| Noder | | Nodeq |
| value | | value |
+-------+ +--------+
Use whatever technique or techniques you chose to define the
data structure. You may want to specifically define when
is in each node when it is created. You may want to
specifically define what is in the Root node if it is
different from other nodes.
Then, in some language of your choice, write legal code
that implements your design and the statement that
creates the Root node. Not a complete program, just the
data definition and one or more statements that are
then needed to create the Root node.
There are many visual structures that may be used on a User Interface. For each structure listed below give one example of what a reasonably good use would be. 1) Menu with drop down menu items 2) check boxes 3) radio buttons 4) choice lists 5) single item text entry 6) Multiple line text entry
There are many types and levels of testing. For each Test listed below, give a short explanation of: a) what is being tested b) how the test might be created c) how the test might be performed (manual, automatic, script, ...) d) how the test might be evaluated (quality, completeness, stress, ...) 1) Unit Test 2) Integration Test 3) System Test 4) Acceptance Test
Last updated 10/22/2013
[CMSC 345] | [Syllabus] | [Lecture Notes] | [Homework] | [Project] | [Notes, all]
Design and Develop an application for a companies Software Quality Assurance Organization. SQAO. The goal is to have this be the instructions for the SQAO including forms and check lists, and in addition be the instructions for the software development teams that must get their software approved by the SQAO before it can be released to the customer. (More details covered in lectures) Your team has significant flexibility. You may require, and have review check list, for the documents required in this course or a different set of documents that your team thinks would produce better quality software. You may use a database or other way to store, retrieve, archive documents and code. It is OK to use information from the literature and from what some company does. Your team may want to pick a specific programming language and have a style guide and specific metric measurements and requirements. Your team may want to specify testing requirements for various stages of the software development. e.g. require a rapid prototype, require unit test, require alpha, beta, final acceptance, or other test. Your team may want to specify a specific configuration management, configuration control system, and possibly specific configuration control software. Being very specific, within practical limitations, will get your team more points than being "wishy washy". SQAO's are typically very strict. Some programmers would say "hard nosed" or "draconian" or worse. Provide for the SQAO to record their evaluation of each project, at each step, through final approval for delivery to the customer. Have at least one complete sample project recorded. Some other partial samples with different evaluations would help. You will need some type of problem or defect reporting capability. Your choice of implementation, it is allowed to model UMBC "ticket" system. Your team will have a "customer" for your project. The "customer" can not change the basic project, yet, may ask for reasonable enhancements or suggest choices for various details. Your "customer" will be asked to give an evaluation of your project after your team has presented it.Technical details for doing your project.
Yes, this is a typical commercial software development. Far different from any personal software development. You will generate more than 10 times as many lines in documents than you generate in code. Someone on your team may be doing some preliminary programming, technically called rapid prototyping. This code may or may not get used and modified.System Requirements Specification SRS
After getting information from lectures and having your team discussions, document what requirements you have so far in the System Requirements Specification, SRS. Typically download srsTemplate.docx copy to srs.doc and hack this into the SRS you will give to your customer for review and possible corrections and additions. Update, fill in contributions, get signatures in appendix A. srsA.docx Appendix A Submit final version with command on linux.gl.umbc.edu submit cs345 team? srs.doc The ? is your team number.System Design Document, SDD
Now focus on design details. Be as specific as possible. After getting information from lectures and having your team discussions, document what design information you have in the System Design Document, SDD. Typically download sddTemplate.doc copy to sdd.doc and hack this into the SDD you will give to your customer for review. Update as needed, fill in contributions, get signatures in Appendix A. sddA.docx Appendix A Submit final version with command on linux.gl.umbc.edu submit cs345 team? sdd.docUser Interface Design Document, UID
Now focus on details of screens that the SQAO will see. Do a layout of login, project selection, check lists, forms, etc. After getting information from lectures and having your team discussions, document the user interface information you have in the User Interface Design Document, UI. Typically download uiTemplate.doc copy to ui.doc and hack this into the UI document you will give to your customer for review and possible corrections or additions. Some screen shots from rapid prototyping efforts may be very useful in this document. Update as needed, fill in contributions, get signatures in Appendix A. uiA.docx Appendix A Submit final version with command on linux.gl.umbc.edu submit cs345 team? ui.docNow team software development should be "full steam ahead".
Every team member is expected to contribute some code. The team member who is code lead, coordinates and makes adjustments as needed.Code Inspection Report, CIR
Now focus on what will help the quality of your code. After getting information from lectures and having your team discussions, document what inspections you want in the Code Inspection Report, CIR. Are you using any software metrics? Do you have automated measurement of the metrics? Do you require any specific range for the measured results to be considered acceptable quality? Typically download cirTemplate.doc copy to cir.doc and hack this into the CIR you will give to your customer for review. Update as needed, fill in contributions, get signatures in Appendix A. cirA.docx Appendix A Submit final version with command on linux.gl.umbc.edu submit cs345 team? cir.docTesting Report Document, TRD
More focus on what will help the quality of your code. There is a classic statement "No amount of testing will produce quality software." But, without systematic testing, the software will have poor quality. Hopefully your customer has tried your project. It may be good news or bad news if your customer reports a defect. Fix all problems that can reasonably corrected, be careful to not make changes that introduce other problems or endanger stability. You will be demonstrating your project. It typically will still have some bugs. Just do you demonstration, trying to avoid any known bugs. The product is at a point where it would be made available for alpha testing. After getting information from lectures and having your team discussions, and actually testing your project, typically per the code inspection, document your test results in the Testing Report Document, TRD. Typically download trTemplate.doc copy to tr.doc and hack this into the TRD you will give to your customer for review. Update as needed, fill in contributions, get signatures in Appendix A. trA.docx Appendix A Submit final version with command on linux.gl.umbc.edu submit cs345 team? tr.docAdministrator Manual, AM
Now focus on what will help the quality of your code. After getting information from lectures and having your team discussions, document what inspections you want in the Code Inspection Report, CIR. Are you using any software metrics? Do you have automated measurement of the metrics? Do you require any specific range for the measured results to be considered acceptable quality? Typically download amTemplate.doc copy to am.doc and hack this into the AM you will give to your customer for review. Update as needed, fill in contributions, get signatures in Appendix A. amA.docx Appendix A Submit final version with command on linux.gl.umbc.edu submit cs345 team? am.docYou are almost finished, just a presentation
With your customer present, each team member does part of the presentation. Demonstrate from login, select project, use of various forms or check lists, defect reporting, etc. Typically administrator enters a new project, new users, then user enters a new document and (comment, defect report, bug, whatever you call it). Have users, at least one project, e.g. some your documents, comments, status, etc. preloaded before start of demonstration. There may be status indicators and [user,date,time] tags on appropriate items. Show sample report of your preloaded information and there may be a few questions or request for more information or demonstration.Notes
Does this seem like too much work for a one semester project? Well, yes for one person, that is why you must make the team activity work. Getting templates: When on linux.gl.umbc.edu, in a terminal window, cp /afs/umbc.edu/users/s/q/squire/pub/download/srsTemplate.docx . cp /afs/umbc.edu/users/s/q/squire/pub/download/srsA.docx . etc. Or, save from the web. Be careful, you may not get an exact copy. Either is acceptable .doc or .docx , try not to get a version that is not readable by Libre Office, Open Office or old Microsoft Word programs.Ask questions
Some that have been asked: What type of computer program is this project? Ans: It is a data entry, data archiving, report generating program. As a minimum it should handle many projects, allow by user name and password, only specific people to enter data into each project. Have an administrator who can start a new project and authorize people. provide a nicely formatted report on screen or printed with all information available about a project. Is it part of my project to write a style formatter? No. Is it part of my project to write a metrics measurement program? No.
Last updated 12/6/2013
Last updated 11/11/2013