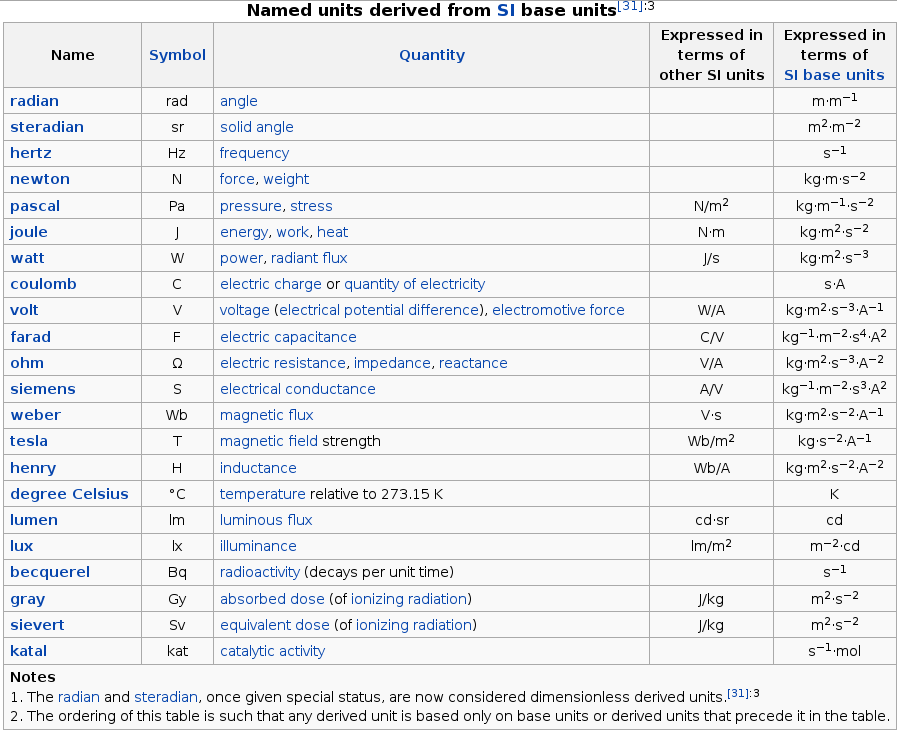
 Compact table of si derived units, dimensions and names:
Compact table of si derived units, dimensions and names:
 Another si dimensions table
Another si dimensions table
Errors can occur in writing equations to solve problems in classical
physics. Many of these errors can be prevented by performing a dimensionality
check on the equations. All physical quantities have a fundamental dimension
that is independent of the units of measurement. The basic physical dimensions
are: length, mass, time, electrical charge, temperature and luminous intensity.
There are a number of systems of units for measuring physical dimensions.
The MKS system is based on meter, kilogram, second measurement. The CGS system
is based on centimeter, gram, second measurement. The English system is based
on feet, pound, second measurement. A few physical dimensions and the
associated measurement unit in these three systems are :
Physical Quantity Unit System
Dimension MKS CGS English
length meter centimeter feet
mass kilogram gram pound mass
time second second second
force newton dyne poundal
energy joule erg B.t.u.
temperature celsius kelvin fahrenheit
The checking of a physical equation has two aspects. The first is to check
the dimensionality. The dimensionality is independent of the unit system. The
second is to check that a consistent system of units is used in the equation.
An example of a dimensionality check is using the basic equation F=ma to
determine that force has the dimension mass x length / time squared, then
check if F=mv2 /r is dimensionally correct. The check is performed by
expanding the dimensions, e.g. mass x (length/time) x (length/time) / length.
Combining terms and reducing yields mass x length / time squared. This agrees
with the dimensions expected for force from the basic equation F=ma. As
expected, centripetal force has the same dimensionality as the force from
Newton's second law of motion.
The table below is organized to present the physical quantity name with
associated information. The second column is one of the typical symbols used
for the physical quantity. The third column is the dimension of the physical
quantity expressed in terms of the fundamental dimensions. The fourth column
is the name of the unit in the MKS measurement system. The fifth column
is the typical MKS unit equation. An independent table presents conversion
factors from the MKS measurement system to other measurement systems.
Physics developed over a period of many years by many people from a variety
of disciplines. Thus, there is ambiguity and duplication of symbols.
PHYSICAL QUANTITY SYMBOL DIMENSION MEASUREMENT UNIT UNIT EQUATION _________________ ______ _________ ________________ ______________ length s L meter m mass m M kilogram Kg time t T second sec electric charge q Q coulomb c luminous intensity I C candle cd temperature T K kelvin oK angle theta none radians none
PHYSICAL QUANTITY SYMBOL DIMENSION MEASUREMENT UNIT UNIT EQUATION
_________________ ______ _________ ________________ ______________
area A L2 square meter m2
volume V L3 stere m3
velocity v L/T meter per second m/sec
angular velocity ω 1/T radians per second sec-1
acceleration a L/T2 meter per square m/sec2
second
angular acceleration α 1/T2 radians per 1/sec2
square second
force F ML/T2 newton Kg m/sec2
energy E ML2/T2 joule Kg m2 /sec2
work W "
heat Q "
torque T ML2/T2 newton meter Kg m2 /sec2
power P ML2/T3 watt joule/sec
density ρ M/L3 kilogram per Kg/m3
cubic meter
specific gravity SG ratio of density to density of water
SG times 1000 Kg/m3 is &rho
pressure P M/LT2 newton per sq m Kg/m sec2
elastic modulus E square meter
bulk modulus K M/LT2 newton per sq m Kg/m sec2
(pressure)
stress σ M/LT2 newton per sq m Kg/m sec2
(pressure)
strain ε none (L'-L)/L dimensionless
momentum mass*vel M ML/T newton second Kg m/sec
impulse p ML/T newton second Kg m/sec
inertia (linear) I ML2/T joule second Kg m2/sec
moment of inertia I ML2 kilogram meter sq Kg m2
luminous flux Φ C lumen (4Pi candle cd sr
for point source)
illumination E C/L2 lumen per cd sr/m2
square meter
entropy S ML2/T2 K joule per degree Kg m2 /sec2 oK
volume rate of flow Q L3/T cubic meter m3 /sec
per second
dynamic viscosity μ M/LT newton second Kg/m sec
per square meter
kinematic viscosity μ/ρ ν L2/T square meter m2 /sec
per second
specific weight γ M/L2 T2 newton Kg/m2 sec2
per cubic meter
PHYSICAL QUANTITY SYMBOL DIMENSION MEASUREMENT UNIT UNIT EQUATION
_________________ ______ _________ ________________ ______________
electric current I Q/T ampere c/sec
2 2 2 2
emf,voltage,potential E ML /T Q volt Kg m /sec c
2 2 2 2
electric resistance R ML /TQ ohm Kg m /sec c
2 3 2 3
conductivity sigma TQ /ML mho per meter sec c /Kg m
2 2 2 2 2 2
capacitance C T Q /ML farad sec c /Kg m
2 2 2 2
inductance L ML /Q henry Kg m /c
2 2
current density J Q/TL ampere per c/sec m
square meter
3 3
charge density rho Q/L coulomb per c/m
cubic meter
magnetic flux, B M/TQ weber per Kq/sec c
magnetic induction square meter
magnetic intensity H Q/LT ampere per meter c/m sec
magnetic vector potential A ML/TQ weber/meter Kg m/sec c
2 2
electric field intensity E ML/T Q volt/meter or Kg m/sec c
newton per coulomb
2 2
electric displacement D Q/L coulomb per c/m
square meter
2 2
permeability mu ML/Q henry per meter Kg m/c
2 2 3 2 2 3
permittivity, epsi T Q /ML farad per meter sec c /Kg m
dielectric constant
-1
frequency f Pi/T hertz sec
-1
angular frequency omega 1/T radians per second sec
wave length lambda L meters m
The dimension of any physical quantity can be written as
La Mb Tc Qd Ce Kf
where a,b,c,d,e and f are integers such as -4, -3, -2 , -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
and L is length, M is mass, T is time, Q is charge, C is luminous intensity
and K is temperature. An exponent of zero means the dimension does not apply
to the physical quantity. The normal rules of algebra for exponents apply
for combining dimensions.
In order to add or subtract two physical quantities the quantities must
have the same dimension. The resulting physical quantity has the same
dimensions. Physical quantities with the same dimension in different
systems of units can be added or subtracted by multiplying one of
the quantities by a units conversion factor to obtain compatible units.
The multiplication of two physical quantities results in a new physical
quantity that has the sum of the exponents of the dimensions of the initial
two quantities.
The division of one physical quantity by another results in a new physical
quantity that has the dimension of the exponents of the first quantity minus
the exponents of the second quantity.
Taking the square root of a physical quantity results in a new physical
quantity having a dimension with exponents half of the initial dimension.
Raising a physical quantity to a power results in a new physical quantity
having a dimension with the exponents multiplied by the power.
e.g. v has dimension L/T
then v2 has dimension L2/T2 or L2 T-2
The derivative of a physical quantity with respect to another physical
quantity results in a new physical quantity with the exponents of the
first dimension minus the exponents of the other dimension.
e.g. v has dimension L/T, t has dimension T,
then dv/dt has dimension L/T2 of acceleration
The integral of a physical quantity over the range of another physical
quantity results in a new physical quantity that has a dimension with the
sum of the exponents of the two quantities.
e.g. v has dimension L/T, t has dimension T,
then integral v dt has dimension L
This section is organized to be consistent with the discussion of physical
quantities and equations of physics. The definition of the six fundamental
units of physical quantities is presented for the MKS system of units. The
definition of some derived units is then presented in the MKS system. The
definitions in other systems of units follow the MKS definitions. This is
followed by a table of conversion factors between the MKS system and other
systems of units.
The MKS system based on the meter, kilogram second was augmented to allow
force and energy from electrical quantities to be measured in one rationalized
system of units. The system was proposed by Giorgi in 1904. It was adopted by
the IEC in 1935 to take effect on January 1, 1940. The electrical to mechanical
conversion was chosen to be based on the permeability of free space to be
-7
4Pi x 10 henry per meter.
Meter, fundamental unit of length, defined as the distance between two
o
specified lines on a specific bar of platinum-iridium at 0 C at standard
atmospheric pressure supported at two neutral points 0.285 meter from the
center of the bar. The bar is kept at the International Bureau of Weights
and Measures near Paris France.
Centimeter, cgs unit of length, defined as 1/100 meter.
Feet, English unit of length, defined as 0.3048 meter in U.S.
Inch, English unit of length, defined as 0.00254 meter in U.S.
-10
Angstrom, unit of length, defined as 10 meter.
Kilogram, fundamental unit of mass, defined as the mass of a specific
cylinder of platinum - iridium kept at the International Bureau of Weights and
Measures.
Gram, cgs unit of mass, defined as 1/1000 kilogram.
Pound, English unit of mass, the avoirdupois pound is defined to be
0.4535924277 kilogram in the U.S. The apothecary or troy pound is
5760/7000 of the avoirdupois pound.
Second, fundamental unit of time, defined as one 86,400th part of a mean
solar day. Presently measured by an atomic clock based on the rate of nuclear
decay.
Coulomb, fundamental unit of charge, defined as the charge required to
obtain one newton of force between two such charges at a distance of one
meter.
Candle, fundamental unit of luminous intensity, defined as the source
intensity of 1/60 centimeter square opening of the standard light source
of a glowing cavity with temperature equal to that of solidifying platinum.
A point source of one candle radiates one lumen per steradian.
Kelvin, fundamental unit of temperature, defined as zero where
the molecular activity of gases cease. The scale is based on zero degrees
centigrade (Celsius) for the freezing point of water and
100 degrees centigrade at the boiling point of water. (at 1 atmosphere)
Zero degrees centigrade is 273.15 degrees Kelvin or 32 degrees fahrenheit.
100 degrees centigrade is 373.15 degrees Kelvin or 212 degrees fahrenheit.
fahrenheite to celsious source code
fahrenheite to celsious output
Radians, fundamental unit of angle, defined as the angle formed by a
length of circular arc being equal to the radius creating the arc.
Newton, unit of force, defined as the force required to accelerate a mass
of 1 kilogram at 1 meter per second per second when acting continuously.
Dyne, cgs unit of force, defined as the force required to accelerate a mass
-5
of 1 gram at at 1 centimeter per second per second. One dyne is 10 newton.
Poundal, English unit of force, defined as the force required to accelerate
a mass of 1 pound at 1 foot per second per second. One poundal is
-10
7.23300 10 newton. A poundal based on earth's gravitation is 32.174 pounds
avoirdupois.
Joule, unit of energy, defined as work done by 1 newton acting through a
distance of one meter. (equivalent to one watt expended in one second.)
Erg, cgs unit of energy, defined as work done by 1 dyne acting through a
-7
distance of one centimeter. One erg is 10 joule.
Kilogram calorie, large calorie, unit of energy, is the heat required to
raise the temperature of 1 kilogram of water 1 degree centigrade at a
stated temperature. i.e. Kg Cal(22 C). The mean kilogram calorie is defined as
1/100 of the heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kilogram of water
o o
from 0 C to 100 C. The small calorie is the gram calorie equal to 1/1000 of
a large calorie. One mean kilogram calorie is 0.000238889 joule .
British thermal unit, B.t.u , unit of energy, the heat required to raise
the temperature of 1 pound of water 1 degree Fahrenheit at a stated
o
temperature. i.e. B.t.u.(39 F). The mean British thermal unit is defined as
1/180 of the heat required to raise the temperature of 1 pound of water from
o o
32 F to 212 F. One mean B.t.u. is 0.00009480 joule.
Mole, kilogram molecule, is the number of kilograms of a substance that
corresponds to its molecular weight divided by 1000. In the cgs system of
units a mole, gram molecule, is the number of grams of a substance that
corresponds to its molecular weight. The mass of a single molecule in
kilograms is the kilogram molecule divided by Avogadro's number. For atoms
the molecular weight is the atomic weight.
Steradian, sr, is the ratio of the area of the intercepted surface of
a sphere to the radius of the sphere squared. 4Pi steradians means the
total area of the sphere is intercepted.
Watt, unit of power, defined as work done at a constant rate of one
joule per second.
Horsepower ( mechanical ), English unit of power, defined as work done
at a rate of 550 foot-pounds per second. One mechanical horsepower is
745.705 watt.
Horsepower ( electrical ), English unit of power, by definition exactly
760 watt.
Ampere, unit of electric current, defined as the current that will flow
through a circuit with a resistance of one ohm when one volt is applied. The
international standard is defined as the current which will deposit silver
at a rate of 0.00111800 gram per second. One international ampere is about
0.999835 absolute ampere. International electrical units are based on physical
standards whose specifications are slightly in error. Instruments made after
January 1, 1948 are calibrated in absolute units.
Notes:
The singular form of units is used with the exception of foot and feet.
Proper names appearing in units and constants are not capitalized.
References:
Conversion Factors and Tables by Zimmerman and Lavine
Electric and Magnetic Fields by Stephen Attwood
Elements of Physics by Shortley and Williams
to get MKS units from other units to get other units from MKS units
value value value value
in MKS = in other x constant in other = in MKS x constant
units units units units
length
meter = angstrom x 1.0E-10 angstrom = meter x 1.0E10
meter = mil x 0.254E-4 mil = meter x 39370.07874
meter = centimeter x 0.01 centimeter = meter x 100
meter = inch x 0.0254 inch = meter x 39.37007874
meter = feet x 0.3048 feet = meter x 3.280839895
meter = yard x 0.9144018288 yard = meter x 1.0936111
meter = fathom x 1.8288036 fathom = meter x 0.546805
meter = rod x 5.0292099 rod = meter x 0.19883839
meter = chain(surveyor) x 20.12 chain(surveyor) = meter x 66 ft
meter = chain(engineer) x 30.48006 chain(engineer) = meter x 100 ft
meter = furlong x 0.2011684E+3 furlong = meter x 0.49709597E-2
meter = mile(statute) x 1.6093472E+3 mile(statute) = meter x 0.6213699E-3
meter = mile(nautical) x 1.8532487E+3 mile(nautical) = meter x 0.539593E-3
meter = league(land) x 4.82804E+3 league(land) = meter x 0.207123E-3
meter = league(marine) x 5.5596E+3 league(marine) = meter x 0.17986E-3
meter = light year x 9.459936E+15 light year = meter x 0.105708E-15
mass
kilogram = gram x 0.001 gram = kilogram x 1000
kilogram = grain(troy) x 0.6480E-4 grain(troy) = kilogram x 15432
kilogram = pennyweight(troy) x 1.5552E-3 pennyweight(troy) = kilogram x 643
pennyweight(troy) = grains * 24
kilogram = carat(troy) x 0.2E-3 carat(troy) = kilogram * 5000
carat(troy) = grains * 324
kilogram = scruple x 1.296E-3 scruple = kilogram x 771.6
kilogram = dram(avdp) x 1.772E-3 dram(avdp) = kilogram x 564.334
kilogram = ounce(avdp) x 0.02834952 ounce(avdp) = kilogram x 35.27
kilogram = ounce(troy) x 0.031103481 ounce(troy) = kilogram x 32.15
kilogram = pound(troy) x 0.37324177 pound(troy) = kilogram x 2.6792285
kilogram = pound(avdp) x 0.45359244 pound(avdp) = kilogram x 2.204622341
kilogram = ton(short) x 907.18486 ton(short) = kilogram x 1.102311E-3
ton(short) = 2000 pounds(avdp)
kilogram = ton(long) x 1016.047 ton(long) = kilogram x 0.9842064E-3
kilogram = ton(metric) x 1000 ton(metric) = kilogram x 0.001
time
second = minute x 60 minute = second * 0.0166667
second = hour x 3600 hour = second * 2.777778E-4
second = day x 86400 day = second * 1.1574E-5
second = fortnight x 1.2096E+6 fortnight = second * 0.82672E-6
second = month x 2.6298E+6 month = second * 0.380257E-6
second = year x 31.557E+6 year = second * 0.031688E-6
electric charge
coulomb = electron charge x 6.2425E+20 electron charge = coulomb x 1.60193E-19
coulomb = faraday x 0.01439 faraday = coulomb x 96.480
coulomb = ampere hours x 2.77778E-4 ampere hours = coulomb x 3600
temperature
o o o o
K = C + 273.16 C = K - 273.16
o o
C = ( F - 32) * 5/9
o o o o
K = ( F - 32) * 5/9 + 273.16 F = ( K - 273.16) x 1.8 + 32.0
o o
F = C * 9/5 + 32
angle
radian = second(angular) x 4.84814E-6 second(angular) = radian x 0.20626E+6
radian = minute(angular) x 0.000290888 minute(angular) = radian x 3437.75
radian = degree(angular) x 0.017453293 degree(angular) = radian x 57.2957795
radian = revolution x 6.2831853 revolution = radian x 0.159154943
radian = bam x
area
square meter = square centimeter square centimeter = square meter
x 1.0E-4 x 10,000
square meter = square inch square inch = square meter
x 6.4516E-4 x 1550
square meter = square feet square feet = square meter
x 0.09290341 x 10.76387
square meter = square yard square yard = square meter
x 0.83613 x 1.19598
square meter = square mile(statute) square mile(statute) = square meter
x 2.589998E+6 x 0.368E-6
square meter = acre x 4046.873 acre = square meter x 0.0002471
square meter = circular mil circular mil = square meter
x 0.506709E-6 x 1.97352E+6
square meter = hectare x 1.0E+4 hectare = square meter x 1.0E-4
square meter = township x 93.24E+6 township = square meter x 1.0725E-8
square meter = barn x 1.0E-28 barn = square meter x 1.0E+28
volume
cubic meter = cubic centimeter x 1.0E-6 cubic centimeter = cubic meter x 1.0E+6
cubic meter = cubic inch x 0.163871E-4 cubic inch = cubic meter x 61023.74
cubic meter = cubic feet x 0.028317 cubic feet = cubic meter x 35.31466
cubic meter = cubic yard x 0.76456 cubic yard = cubic meter x 1.30795
cubic meter = cubic mile(statute) x cubic mile(statute) = cubic meter
x 4.168205E+9 x 0.23991E-9
cubic meter = liter x 0.001 liter = cubic meter x 1000
cubic meter = fluid ounce x 0.295737E-4 fluid ounce = cubic meter x 0.33814E+7
cubic meter = cup x 0.236589E-3 cup = cubic meter x 42267
cubic meter = pint(liquid) pint(liquid) = cubic meter x 21113.4
x 0.4731798E-3
cubic meter = quart(liquid) quart(liquid) = cubic meter
x 9.4625E-4 x 1056.8
cubic meter = gallon x 0.003785 gallon = cubic meter x 264.2
cubic meter = barrel x 6.28981 barrel = cubic meter x 0.1589873
cubic meter = pint(dry) x 5.50625E-4 pint(dry) = cubic meter x 1816.118
cubic meter = quart(dry) x 2.75313E-4 quart(dry) = cubic meter x 908.059
quart(dry) = pint(dry) x 0.5
cubic meter = peck x 8.81E-3 peck = cubic meter x 113.507
peck = quart(dry) x 0.125
cubic meter = bushel x 0.03524 bushel = cubic meter x 28.3768
bushel = peck x 0.25
cubic meter = keg x (less than 10 gal)
cubic meter = cord x 3.625
barrel = gallon x 31.5 (food) x 42 (petroleum)
velocity
meter per second = centimeters per second x 100.0
meter per second = kilometer per hour x 0.001
meter per second = inches per second x 39.37
meter per second = feet per second x 3.28083
meter per second = miles per second x 17322.6
meter per second = inches per minute x 0.6562
meter per second = feet per minute x 0.05468
meter per second = miles per hour x 2.2369
meter per second = knots x 1.9438
acceleration
meter per second squared = centimeter per second squared x 100.0
meter per second squared = feet per second squared x 3.28083
meter per second squared = miles per hour squared x 2.2369
force
newton = dyne x 1.0E-5 dyne = newton x 1.0E5
newton = poundal x 7.233 poundal = newton x 0.138
newton = pound force x 7.233/32.17 g pound force = newton X 1/0.2248
x 0.2248
energy
joule = watt second watt = joule per second
joule = erg x 1.0E-7 erg = joule / 1.0E-7
joule = gram calorie x 0.238889E-6
joule = calorie x 1/0.238889 calorie = joule x 0.239
joule = foot pounds x 1.356 foot pounds = joule x 0.7376
joule = kilowatt hour x 3.6E+6 kilowatt hour = joule/(60*60*1000)
joule = watt hour x 1/0.0027 watt hour = joule x 0.00027
joule = horsepower hours x 2.684E+6
joule = BTU x 1/0.00094 BTU = joule x 0.00094
joule = therm x 1/9.478E-9 therm = joule x 9.478E-9
power
watt = volt ampere x 1
watt = calorie per second x 1/0.2390 calorie per second = watt x 0.2390
watt = joule per hour x 1/3600 joule per hour = watt x 3600
watt = erg per second x E-7 erg per second = joule x E+7
watt = kilogram calorie per second x
watt = kilogram calorie per minute x
watt = horsepower(mechanical) x 1/745.705
watt = horsepower(electrical) x 1/760 horsepower(electrical) = watt x 760
watt = horsepower(metric) 1.014 ?
watt = horsepower(boiler) x 9.804E+3 33,520 Btu per hour
watt = B.t.u per minute x 17.57
watt = B.t.u per hour x 17.57*60
watt = foot pound per minute x 0.2260E-3 33000 HP
watt = foot pound per second x 1.356 550 HP
density
kilogram per cubic meter = pound per cubic foot x 16.018 ?
pressure
pascal = newton per square meter x 1
pascal = Kg force per square meter x 1/0.10197
pascal = pound force per square foot x 1/0.020885
pascal = pound force per square inch x 1/0.145038E-3
pascal = ton per square foot x 10.4E-6
pascal = atmosphere(standard) x 1E-5
pascal = inch of water x 0.004
pascal = inches of mercury x 1/0.296E-3
pascal = millimeters of mercury x 0.0075
pascal = bar x 1/1.0E-5 bar = pascal x 1.0E-5
pascal = millibar x 1/0.01 millibar = pascal x 0.01
pascal = torr x 0.0075
torque
newton meter = foot pound x
flow rate
cubic meter per second = gallon per minute x 0.6309E-8
cubic meter per second = cubic feet per minute x 0.4719E-3
specific heat, entropy
o o
joule per kilogram K = B.t.u. per pound F x 4.187E+3
dynamic viscosity
poise = dyne second per square centimeter
kinematic viscosity
stoke = square centimeter per second
electric current
ampere = abampere x 10
ampere = statampere x 0.333333E-9
magnetic flux B
magnetic induction
magnetomotive force
magnetic field strength H
dielectric constant
permittivity constant
rotation rate
radians per second = revolutions per second x
radians per second = revolutions per minute x
There are a number of physical constants that are used in equations
to solve problems in physics. Errors may occur because the dimensionality
and/or units of the physical constant are not known. The table below
presents some physical constants with their typical symbol, dimension,
nominal value and unit of measure in the MKS system.
PHYSICAL CONSTANT SYMBOL DIMENSION MKS VALUE UNIT
_________________ ______ _________ _________ ____
3 3
air density, normal rho M/L 1.293 Kg/m
conditions
air molecule, mass m M 4.81E-26 Kg
a
air molecule, w M 0.028952 Kg/mole
kilogram molecular weight
2 2
atmospheric pressure A M/LT 1.01325 newton/m
Avogadro's number N none 6.023E+23 molecules in
molecules in a mole a mole
based on 12g of carbon-12
2 2 o
Boltzmann's constant k ML /T K 1.380E-23 joule/ K
same units as entropy
2 2
electron volt e ML /T 1.60210E-10 joule
3 2 2 2 2
electrostatic constant k ML /T Q 8.987E+9 nt m/coulomb
reciprocal permittivity m/farad
elementary charge e Q 1.6021892E-19 coulomb
electron mass m M 9.1066E-31 Kg
e
faraday f L/T 9.648456E+4 coulomb/mole
2 2 o
gas constant of a mole R ML /T K 8.3144 joule/ K
Avogadro * Boltzmann
2 2
gravity (earth) g L/T 9.80665 m/sec
hydrogen atom mass m M 1.6734E-27 Kg
h
hydrogen atom w M 1.0079E-3 Kg/mole
kilogram atomic weight
2 2
impedance of free space Z ML /TQ 120Pi ohm
0
mechanical equivalent J none 4186.05 joule/
of heat Kg calorie
2 2 3
permittivity (vacuum) epsi T Q /ML 8.854E-12 farad/meter
0
2
permeability (vacuum) mu ML/Q 4Pi E-7 henry/meter
0
Pi, ratio of circumference Pi none 3.14159265 radians
to diameter
2
Planck's constant h ML /T 6.624E-34 joule second
speed of light (vacuum) c L/T 2.99792458E+8 meter/second
speed of sound (air) s L/T 331.45 meter/second
2 2 2 2
universal gravitational G L /MT 6.6720E-12 nt m /Kg
constant
3 3
density of fresh water rho M/L 1000.0 Kg/m
definition 62.43 lb/cu-ft
3 3
density of sea water rho M/L 1025.0 Kg/m
approx 64.00 lb/cu-ft
Note: some constants are related to combinations of other constants :
electrostatic constant = 1/ 4Pi permittivity (vacuum)
speed of light = 1/ sqrt( permittivity x permeability )
impedance of free space Z = sqrt( permeability / permittivity )
0
SOME EQUATIONS OF PHYSICS
F = m a force equals mass times acceleration,
Newton's second law of motion
2
F = m v /r force equals mass times velocity squared over radius,
centripetal force of a mass traveling in a circle
2
F = G m m /s gravitational force between mass and mass at distance s
1 2 1 2
with universal gravitational constant G
2
g = G m /r acceleration due to gravity on earth
earth earth
2
F = k Q Q /s electrical force between charge and charge at distance s
1 2 1 2
with electrostatic constant k . If there is a dielectric
then multiply by the non dimensional dielectric constant.
F = 1/2Pi mu I I /s
1 2
electrical force between two parallel wires carrying
currents I and I with a spacing s with permeability
1 2
mu. This is the force for one meter of wire length.
2
F = B H s
electrical force in a magnetic field equals the magnetic
flux times the magnetic intensity applied to an area
2
F = E D s
electrical force in an electric field equals the electric
field intensity times the electric displacement applied
to an area
s = v t distance equals velocity times time (linear)
v = a t velocity equals acceleration times time (linear)
2
s = s + v t + 1/2 a t
0 0
linear distance equals initial distance plus
initial velocity times time plus one half acceleration
times time squared
2
v = sqrt( v + 2as)
f 0
the final velocity equals the square root of the
initial velocity squared plus two times the acceleration
times the distance traveled
v = sqrt( s g ) the critical velocity for any object to orbit at a
c
distance s from the source of gravitational field g
vf1 = ((m1-m2)/(m1+m2))*v1 + ((2*m2)/(m1+m2))*v2
vf2 = ((m2-m1)/(m1+m2))*v2 + ((2*m1)/(m1+m2))*v1
final velocities of an elastic collision of body
with mass m1 and velocity v1 hitting a body with
mass m2 and velocity v2. Kinetic energy conserved.
vf = (m1*v1 +m2*v2)/(m1+m2)
final velocity of an inelastic collision of body
with mass m1 and velocity v1 hitting and sticking
to a body with mass m2 and velocity v2. Kinetic
energy is not conserved but is converted.
theta = omega t angle equals angular velocity times time (rotational)
omega = alpha t angular velocity equals angular acceleration times time
(rotational)
2
theta = theta + omega t + 1/2 alpha t
0 0
angular rotation equals initial angle plus
initial angular velocity times time plus one half
angular acceleration times time squared
2
w = sqrt(w + 2 alpha * angle)
f 0
the final angular velocity equals the square root of
the initial angular velocity squared time twice the
angular acceleration times the angle traveled
2
I = mass*radius moment of inertia, about an axis, integral from 0 to mass
of radius squared times incremental mass
T = I alpha torque equals moment of inertia times angular acceleration
L = I omega angular momentum equals moment of inertia times
angular velocity
2
E = 1/2 I omega kinetic energy equals one half moment of inertia times
angular velocity squared
P = I alpha omega power equals moment of inertia times angular acceleration
times angular velocity
W = I alpha theta work equals moment of inertia times angular acceleration
times angle traveled
E = I R voltage equals current through a resistor times the
resistance
I = C (E - E )/(t - t )
2 1 2 1
the current through a capacitor equals the capacitance
times the change in voltage over the change in time
E = I * time / C actually an integral of current divided by C
one amp for one scecond charges one farad to one volt
E = L (I - I )/(t - t )
2 1 2 1
the voltage across an inductor equals the inductance
times the change in current over the change in time
I = E * time / L actually a derivative of voltage divided by L
one volt change in one second causes a current
of one amp in a 1 henry inductor
C = epsi A/s
the capacitance in farad of a parallel plate capacitor
equals the permittivity times the area divided by the
spacing.
L = n mu r (ln 8r/d - 7/4)
the inductance in henry of n turns of wire with diameter
d closely wrapped in a coil of radius r with permeability
mu is approximately given by this equation.
H = 1/2 I / r
the magnetic intensity at the center of a current loop
equals 1/2 the current divided by the radius of the loop
B = mu H the magnetic flux equals the permeability times the
magnetic intensity
D = epsi E the electric displacement equals the permittivity
times the electric field intensity
P = E I power equals an electrical potential causing a current
P = F s power equals a force applied over a distance
2
E = m c energy from converting a mass to energy
( c = speed of light)
E = I omega energy of rotation, Inertia times rotational velocity
2
E = 1/2 m v kinetic energy of a mass traveling at a velocity
E = m g s potential energy of a mass in a gravitational field
at a height s
E = 1/2 B H V energy of a magnetic field in the volume V with magnetic
flux B and magnetic intensity H. This is usually an
integral of an incremental volume times B times H
in the incremental volume.
E = 1/2 D E V energy of an electric field in the volume V with electric
displacement D and electric field intensity E. This is
usually an integral of an incremental volume times D
times E in the incremental volume.
2
E = 1/2 C V energy stored in a capacitor with capacitance C having
a voltage V
2
E = 1/2 L I energy stored in an inductor with inductance L having
a current I
T = F s torque equals the force applied at radius s
T = I alpha torque equals the rotational inertia times the angular
acceleration
2
E = P V = R T = Na k T = 1/3 N m v ideal gas law
rms
These relations are for one mole (kilogram molecule) of
an ideal gas at an absolute pressure P, volume V,
gas constant R, Avogadro's number Na, Boltzmann's
constant k, temperature T in Kelvin, gas
molecule mass m, root mean square speed of the molecules
v in meters per second. Each section of the equation
rms
represents energy in joule.
P V = n R T for n moles of the gas.
With sigma being density, P = sigma R T / M where M = mass/n
2 2
P + 1/2 rho v + rho g z = P + 1/2 rho v + rho g z
1 1 1 2 2 2
This equation relates pressure P, velocity v and relative
height z for a non compressible fluid in a pipe, observed
at location 1 and location 2. rho is the density of the
fluid and g is the gravitational constant.
2
L = C rho v A / 2
L
the lift force equals the dimensionless coefficient of
lift times the air density times the velocity squared times
the surface area divided by 2.
2
D = C rho v A / 2
D
the drag force equals the dimensionless coefficient of
drag times the air density times the velocity squared times
the surface area divided by 2.
nu = mu / rho
the kinematic viscosity equals the dynamic viscosity over
the density in a fluid
P = Q (p - p )
1 2 the power, P, required to drive a volume rate of flow, Q,
from pressure p to pressure p .
1 1
o o
C = K - 273.16
degrees centigrade equals Kelvin minus 273.16
o o
F = ( K -273.16) x 9/5 + 32
degrees Fahrenheit as a function of Kelvin
y(x) from EI y'''' = p(x) beam deflection with loading p(x), -L/W constant load
E is Young's Modulus
I is moment of inertia
L is length of beam
W is weight of load (including beam)
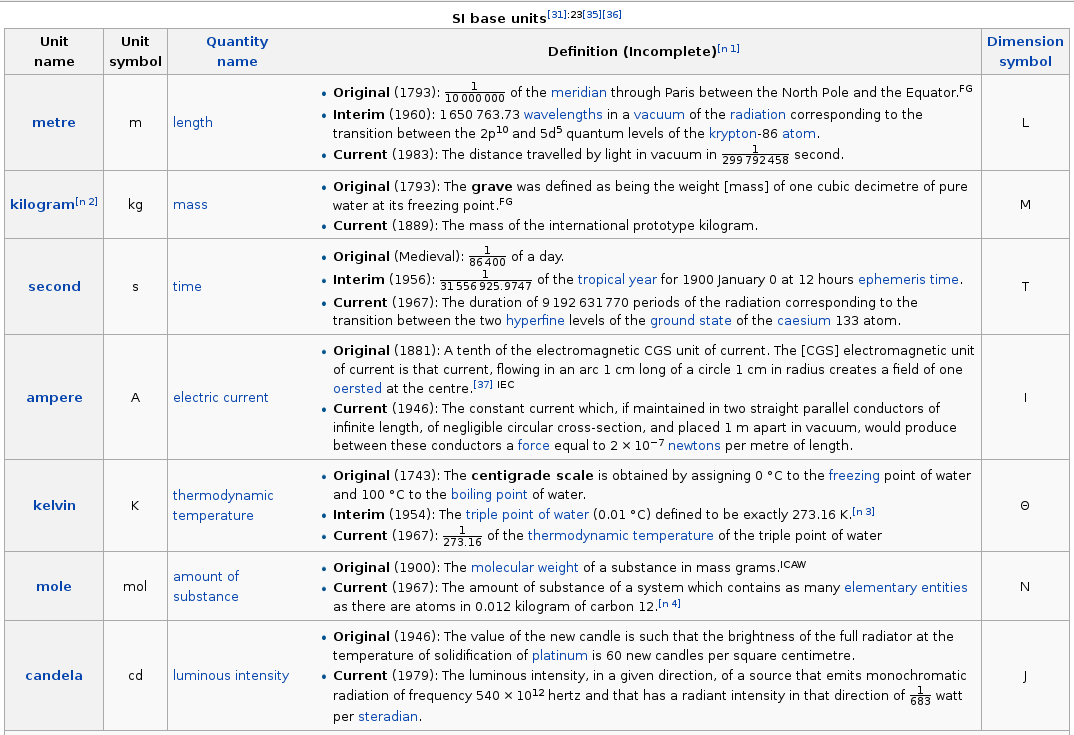
Table of si base units, with some history:
 Compact table of si derived units, dimensions and names:
Compact table of si derived units, dimensions and names:
 Another si dimensions table
Another si dimensions table
Last updated 1/30/2019