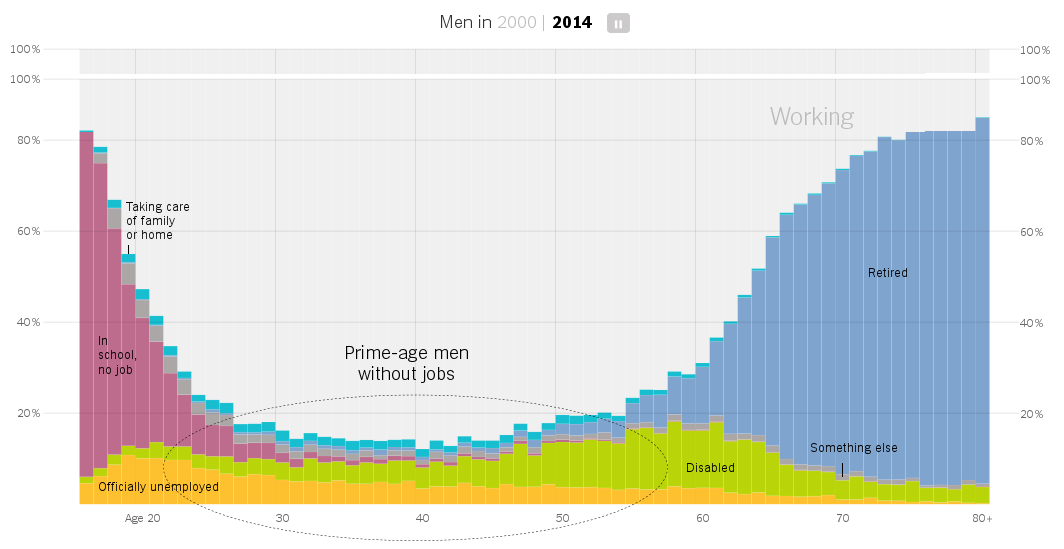
highway.m4v large, may be slow to load
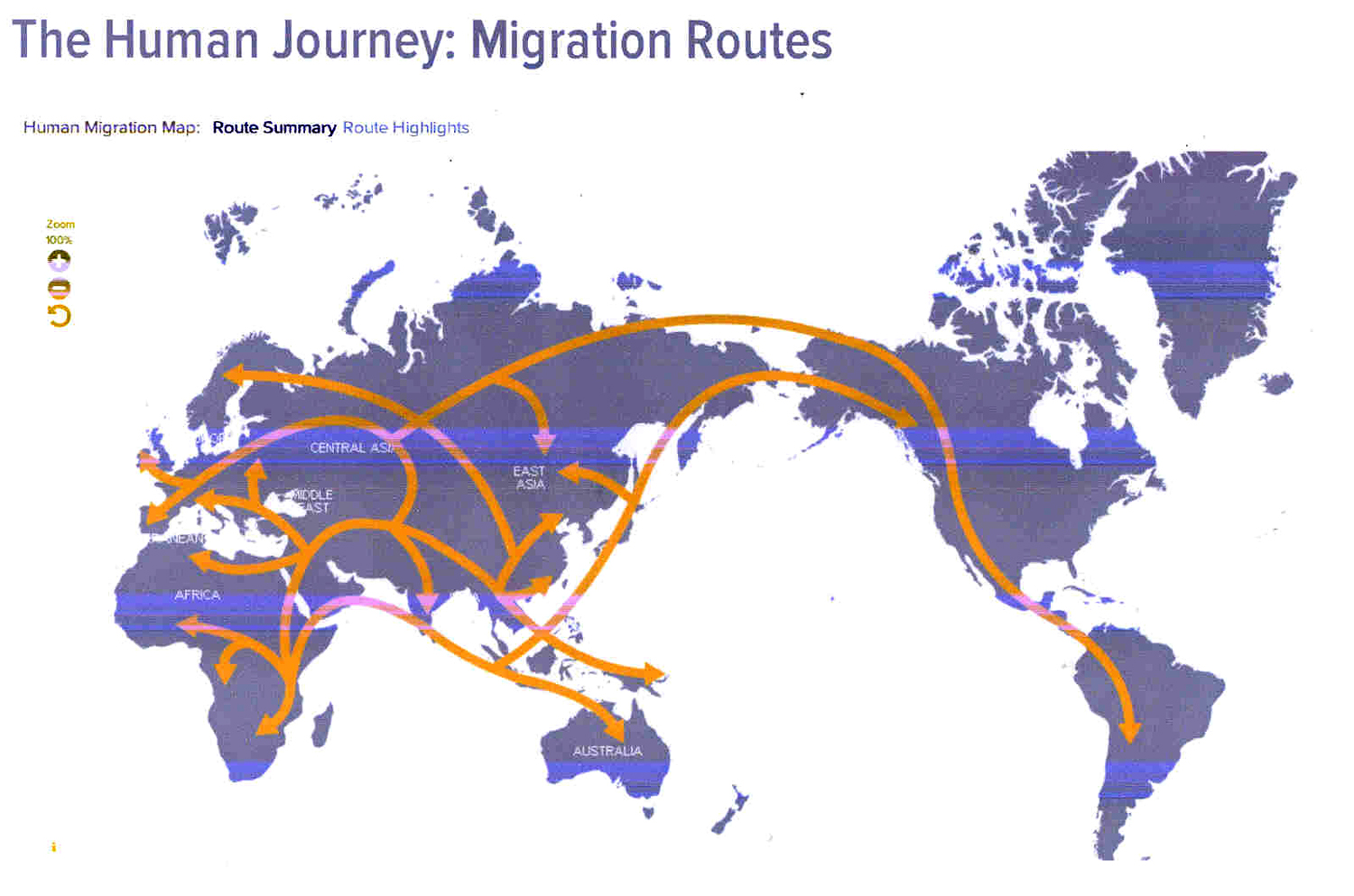
When humans first ventured out of Africa some 60,000 years ago, they left genetic footprints still visible today. By mapping the appearance and frequency of genetic markers in modern peoples, we create a picture of when and where ancient humans moved around the world. These great migrations eventually led the descendants of a small group of Africans to occupy even the farthest reaches of the Earth. Our species is an African one: Africa is where we first evolved, and where we have spent the majority of our time on Earth. The earliest fossils of recognizably modern Homo sapiens appear in the fossil record at Omo Kibish in Ethiopia, around 200,000 years ago. Although earlier fossils may be found over the coming years, this is our best understanding of when and approximately where we originated. According to the genetic and paleontological record, we only started to leave Africa between 60,000 and 70,000 years ago. What set this in motion is uncertain, but we think it has something to do with major climatic shifts that were happening around that time a sudden cooling in the Earth’s climate driven by the onset of one of the worst parts of the last Ice Age. This cold snap would have made life difficult for our African ancestors, and the genetic evidence points to a sharp reduction in population size around this time. In fact, the human population likely dropped to fewer than 10,000. We were holding on by a thread. Once the climate started to improve, after 70,000 years ago, we came back from this near-extinction event. The population expanded, and some intrepid explorers ventured beyond Africa. The earliest people to colonize the Eurasian landmass likely did so across the Bab-al-Mandab Strait separating present-day Yemen from Djibouti. These early beachcombers expanded rapidly along the coast to India, and reached Southeast Asia and Australia by 50,000 years ago. The first great foray of our species beyond Africa had led us all the way across the globe. Slightly later, a little after 50,000 years ago, a second group appears to have set out on an inland trek, leaving behind the certainties of life in the tropics to head out into the Middle East and southern Central Asia. From these base camps, they were poised to colonize the northern latitudes of Asia, Europe, and beyond. Around 20,000 years ago a small group of these Asian hunters headed into the face of the storm, entering the East Asian Arctic during the Last Glacial Maximum. At this time the great ice sheets covering the far north had literally sucked up much of the Earth’s moisture in their vast expanses of white wasteland, dropping sea levels by more than 300 feet. This exposed a land bridge that connected the Old World to the New, joining Asia to the Americas. In crossing it, the hunters had made the final great leap of the human journey. By 15,000 years ago they had penetrated the land south of the ice, and within 1,000 years they had made it all the way to the tip of South America. Some may have even made the journey by sea. The story doesn’t end there, of course. The rise of agriculture around 10,000 years ago—and the population explosion it created—has left a dramatic impact on the human gene pool. The rise of empires, the astounding oceangoing voyages of the Polynesians, even the extraordinary increase in global migration over the past 500 years could all leave traces in our DNA. There are many human journey questions waiting to be asked and answered.mother of all humans Five great species extinctions