|
|
Biology of Methanogenesis |
Department of Marine
Biotechnology UMBC - Institute of Marine & Environmental Technology
Mechanisms
of Archaeal Gene Transcription
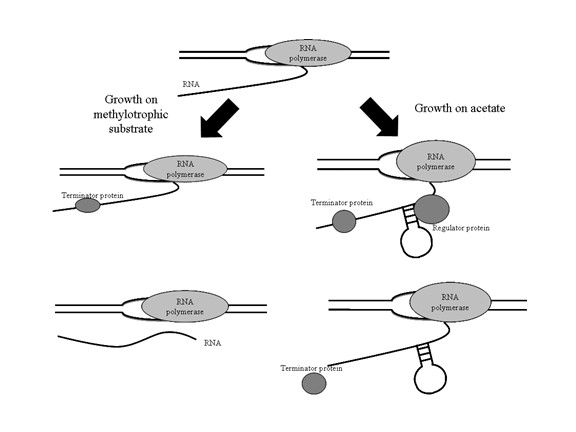
Biogenic methane production catalyzed by microbial consortia is a widely available, renewable resource for both energy production from plant materials and organic waste treatment. The efficiency of this process is directly dependent on the interaction of three metabolically distinct groups of microorganisms; the fermentative and acetogenic Bacteria and the methanogenic Archaea. One of the rate limiting steps in the degradation of soluble organic matter is the dismutation of acetate, a predominant intermediate in the process, which accounts for 70% or more of the global methane produced biogenically. Acetate utilization is controlled in part by regulation of expression of carbon monoxide dehydrogenase/acetyl CoA synthase (CODH/ACS), which catalyzes the dismutation of acetate. However, it is not known if regulation is mediated at the level of transcription initiation, elongation, or mRNA processing. We have shown that deletions upstream of the promoter affected expression of the operon encoding CODH/ACS (cdhABCDE) during growth on acetate, and deletions downstream affected expression of the operon during methylotrophic growth. In contrast to other methanogen genes that are regulated by binding of a repressor or activator protein in proximity of the promoter, the operon encoding CODH/ACS appears to be attenuated by mechanisms located both upstream and downstream of the promoter. Ongoing studies suggest that expression of CODH/ACS is mediated by DNA binding proteins and by mechanisms that recognize RNA secondary structure.
The overall goal of this research is to identify the regulatory components that interact with DNA and RNA elements of cdhABCDE of Methanosarcina acetivorans using a combination of biochemical and genetic approaches. The microorganism is well suited for these studies as it has a tractable genetic system, it can be mass cultured, its genome has been sequenced and it is the model for much of our prior research. Results of this research will reveal whether this critical catabolic pathway is controlled by mechanisms similar to those employed by the Bacteria and Eukarya, or by a regulatory paradigm that is unique to the Archaea. The results of this project will also provide the groundwork for future studies on structure -function analyses of archaeal regulatory proteins. The mechanism(s) revealed by this investigation will provide greater insight into the regulatory strategies employed by the aceticlastic methanogenic Archaea to efficiently direct carbon and electron flow in anaerobic consortia during fermentative processes.
 Project Team
Project Team
Kimberly Anderson, B.S., M.S.
Ethel Apolinario, B.S.
 Publications and Presentations
Publications and Presentations
Anderson, K.L., E.E. Apolinario, S.R. MacAuley, and K.R. Sowers. 2009. Localization of a regulatory region within the 5’ untranslated leader region of an archaeal CO dehydrogenase/acetyl-coenzyme synthase. J. Bacteriol. 191(22): 7123-7128 [ABSTRACT].
Sowers, K.R. 2009. Methanogenesis. In: Schaechter, Lederberg, Alexander, Haselkorn, Ingraham, Baross, Schmidt, Laskin, Hopwood, Summers, Baulcombe, Levin, White, Fierer, Baldauf (eds.), Encylopedia of Microbiology, 3rd edition. Elsevier, Inc. ISBN: 978-0-12-373944-5.
K.R. Sowers. Applications of Marine Microbes for Bioremediation and Bioenergy. 2008 Joint EC-US/CIESM Workshop on Marine Genomics. Fontvielle, Monaco. October 12-14, 2008.
K.R. Sowers. Biotechnological Advances in the Study of the Methanogenic Archaea. Chinese National Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China. November 5, 2008.
Sowers, K.R. and K. Anderson. 2007. Molecular Genetics of Archaea. In: R. Cavicchioli (ed.), Archaea: Molecular Cell Biology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D. C., pp. 463-477. ISBN: 978-1-55581-391-8.
Sowers, K.R., S. DasSarma and P. Blum. 2007. Gene transfer in Archaea. In: C. A. Reddy, T. J. Beveridge, J. A. Breznak, G. A. Marzluf, and T. M. Schmidt (ed.), Methods for General and Molecular Microbiology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D. C. ISBN: 978-1-55581-223-2.
Sowers, K.R.* and S. MacAuley. A third alternative for protein expression: the methanogenic Archaea. Annual Meeting of the Society for Industrial Microbiology. July 29-Aug 2, 2007. Denver, CO.
Sowers, K.R. and K. Anderson. 2007. Molecular Genetics of Archaea. In: R. Cavicchioli (ed.), Archaea: Molecular Cell Biology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D. C., pp. 463-477. ISBN: 978-1-55581-391-8.
K.L. Anderson, E.A. Apolinario-Smith, and K.R. Sowers. Regulation of Biogenic Methane Production from Acetate by Marine Methanosarcina Species. Gordon Research Conference on Archaea: Ecology, Metabolism and Molecular Biology. August 19-24, 2007, Andover, NH.
R. Jasso-Chavez*, E.A. Apolinario-Smith, K.R. Sowers and J.G. Ferry. The Na+/H+ Mrp antiporter in Methanosarcina acetivorans. Gordon Research Conference on Archaea: Ecology, Metabolism and Molecular Biology. August 19-24, 2007, Andover, NH.
Anderson, K.L., E.E. Apolinario, S.R. MacAuley, and K.R. Sowers. 2007. Regulation of biogenic methane production from acetate by marine Methanosarcina species. 8th International Marine Biotechnology Conference, Eilat, Israel. March 11-16.
Maeder, D.L., I. Anderson, T. Brettin, D. Bruce, P. Gilna, C. S. Han, A. Lapidus, W.W. Metcalf, E. Saunders, R. Tapia, and K.R. Sowers. 2006. The Methanosarcina barkeri genome: comparative analysis with Methanosarcina acetivorans and Methanosarcina mazei reveals extensive rearrangement within methanosarcinal genomes. J. Bacteriol. 188: 7922-7931
Sowers, K.R. and J.E.M. Watts. 2006. The study of strictly anaerobic microorganisms. In: F. A. Rainey and A. Oren (ed.), Methods in Microbiology - Extremophiles, v. 35. Elsevier/Academic Press, Oxford, pp. 739-764. ISBN: 0-12-521537-1.
Anderson, K.L., Ethel E. Apolinario-Smith, Sheridan R. MacAuley, and Kevin R. Sowers. 2006. Regulation of Gene Expression for Carbon monoxide Dehydrogenase (cdhA) from Methanosarcina species. 106th Ann. Mtg. Amer. Soc. Microbiol. May 21-25. Orlando, Fl.
Apolinario-Smith,
E., K.M. Jackson, and K.R. Sowers. 2005. Development
of a plasmid-mediated reporter system for in vivo monitoring of gene
expression in the archaeon Methanosarcina acetivorans.
Appl.
Envion. Microbiol.,
71: 4914-4918.
Anderson, K.L., E.A. Apolinario-Smith, and K.R. Sowers. 2005. Mechanisms of Gene Expression for Carbon Monoxide Dehydrogenase (cdhA) from Methanosarcina thermophila”. Gordon Research Conference on Archaea: Ecology, Metabolism and Molecular Biology. August 14-18, Oxford, England.
Apolinario-Smith, E., K.M. Jackson and K.R. Sowers. 2003. Identification of Regulatory DNA Sequence for Methanosarcina thermophila CO Dehydrogenase (cdh) by Deletion Analysis. Gordon Research Conference on Archaea: Ecology, Metabolism and Molecular Biology. August 3-8, Andover, NH
Galagan, J.E., et al. 2002. The genome of Methanosarcina acetivorans reveals extensive metabolic and physiological diversity. Genome Research 12: 532-542.
Jackson, K., Apolinario-Smith, E. and Sowers, K.R. 2002. Regulation of Catabolic Carbon Monoxide Dehydrogenase in the Archaeon Methanosarcina acetivorans. Southeastern Branch of the Amercian Society of Microbiology Annual Meeting, Gainsville, Florida. November 7-9.
Apolinario-Smith, E., Jackson, K., and Sowers, K.R. 2002. Regulation of the CO dehydrogenase promoter in Methanosarcina acetivorans grown on aceticlastic and methylotrophic substrates. Abstr. 102nd Ann. Mtg. Amer. Soc. Microbiol., Las Vegas, NV.
Sowers, K.R. 2000. Methanogenesis. In: Lederberg, Alexander, Bloom, Hopwood, Hull, Iglewski, Laskin, Oliver, Schaechter, Summers (eds.), Encylopedia of Microbiology, 2nd edition. Academic Press, Inc.
Sowers, K.R. and H.J. Schreier. 1999. Gene transfer systems for the Archaea. Trends Microbiol. 7: 212-219.
Metcalf, W.W., J.K. Zhang, E. Apolinario, K.R. Sowers, and R.S. Wolfe. 1997. An archaeal gene transfer system for Methanosarcina spp.: liposome-mediated transformation and construction of shuttle vectors. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 2626-2631.
Sowers, K.R., T.T. Thai, and R.P. Gunsalus. 1993. Transcriptional regulation of the carbon monoxide gene (cdhA) in Methanosarcina thermophila. J. Biol. Chem. 268: 23172-23178.
Related Publications and Presentations
Sowers, K.R. and R.P. Gunsalus. 1988. Plasmid DNA from the acetotrophic methanogen Methanosarcina acetivorans. J. Bacteriol. 170: 4979-4982.
Sowers, K.R., S.F. Baron and J.G. Ferry. 1984. Methanosarcina acetivorans sp. nov., an acetotrophic methane producing bacterium isolated from marine sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 47: 972‑978.
Funded by