Major Points
1. Cells reproduce --> pass on copies of their genome
2. Mitosis: produces exact copies
3. Replication and segregation of chromosomes during a cell cycle
Topics for Next 9 Lectures
* Transfer of genetic information
* Gamete formation
* Patterns of inheritance
* Chromosomes and inheritance
* Structure/function of DNA
* Transfer of genetic information to proteins
* Control of gene expression
* Genetice engineering
Genetics is central
* Determines function of organisms
* Programs interactions among cells
* Determines our perception of the world
* Regulates interactions between organisms
* Affects interactions in populations
* Is the basis for evolution--the central concept in biology
Organisms Must Reproduce
All organisms have a limited lifetime
so they must reproduce themselves
* The thing that distinguishes biological entities most clearly is this
ability
* Even viruses reproduce themselves
Forms of Cell Division
* Binary fission (bacteria)
- Asexual reproduction
+ Meaning that fusion of germ cells ("gametes") is
not involved
+ No new individuals
- Equal (or sometimes unequal) division of cell & all its contents (including
DNA)
- No overt change in appearance
Forms of Cell Division
* Mitosis (eukaryotes)
- Produces identical copies ("clones")
- Asexual reproduction (in single-cell eukaryotes)
- Provides bodily growth in multicellular eukaryotes
Forms of Cell Division
* Meiosis (eukaryotes)
- Sexual reproduction
- Produces cells that are different from the mother cell
- Produces gametes, and therefore is essential to provide genetic variability
Why is that important?
Eukaryotic DNA is in Chromosomes
* Chromosome = "colored body"
* Segregated to daughter cells
* Identified with Mendel's genetic traits
* Contain one linear molecule of DNA
* DNA packaged into a structure with protein
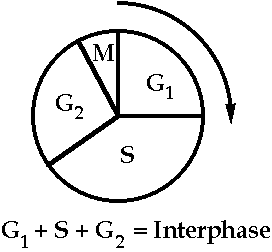
The Cell Cycle
Segregation and replication of DNA occurs on a schedule--the cell cycle
* Cells grow continuously after division
* At a particular size (= time) they begin replication of DNA
* Replication always takes about the same time
* They then continue growth and divide at the appropriate size
The Cell Cycle
Stages of Mitosis
* Prophase
- Condensation of chromosomes (early)
- disassembly of the nucleus (late)
* Metaphase
- Chromosomes attach to spindle
- Line up on metaphase plate
* Anaphase
- Chromosomes move to ends of spindle
* Telophase
- Chromosomes decondense; nucleus reforms
