Major Points
1. Random processes can change allele frequency (review)
2. Three types of natural selection:
Directional Selection
Stabilizing Selection
Destabilizing Selection
Random Processes Affecting Allele Frequency
Mutation
Genetic Drift
Bottlenecks
Founder Effect
Gene Flow
Mutation
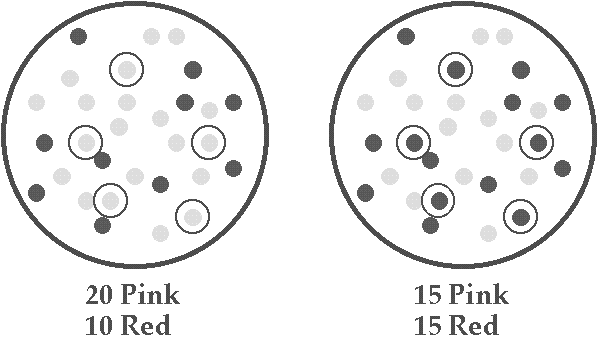
Genetic Drift
A chance event can cause a change in allele frequency
For example, a chance event can cause massive death
Survival may be totally unrelated to genotype
This contradicts Darwin's dictum about the "survival of the fittest"
Genetic drift can have a major impact
Genetic Drift--Bottleneck

Genetic Drift--Founder Effect

Gene Flow
Movement of individuals between populations
Moves the alleles carried by the individuals
Can change the allele frequency in both populations
Can be a chance event (unrelated to genotype)
Can tend to keep allele frequencies similar
Can also spread new alleles that arise in one population
Gene Flow

Natural Selection
Offspring excede the available support
They will compete for survival
Allelic differences exist in populations
These differences can affect surviva
Individuals with some allele combinations may be more likely to survive
Therefore, selection may drive changes in allele frequency (microevolution)
Effects of Selection
It is important that selection may change over time
An alleles that was "adaptive" may rapidly become "non-adaptive"
This may change allele frequency
Conditions may change again, and the allele may again become adaptive
The Example of the Peppered Moth
The population was stable: mostly light-colored moths with a minority of
dark
The industrial revolution caused pollution that changed the habitat
Lichen on trees died, making the trees appear much darker
At the same time, the frequency of the light-colored variant declined compared
with the dark-colored
What Was Happening?
Ecologists hypothesized that the change in habitat selected for a change
in allele frequency
* The moths spend the day on tree bark
* Light-colored moths would be easier prey on dark wood
* Dark-colored moths would not be as easy prey
So natural selection could explain the event
Directional Selection
The peppered moth story is an example
* When the environment changed the adaptiveness of the two alleles reversed
* Later, when pollution was reduced the light\endash colored moths ratio
increased
This is the kind of effect which can drive the process of evolution
Other Types of Natural Selection
Stabilizing selection
* A common allelic trait is favored, less common are disfavored
* Promotes phenotypic uniformity
Destabilizing selection:
* Intermediate traits are disfavored, while two extremes are favored
* Promotes phenotypic differences
Stabilizing Selection

Destabilizing Selection

Balanced Polymorphism
Polymorphism: "having many forms"
Destabilizing selection favors the presence of multiple alleles
Acts by disfavoring an intermediate
Polymorphism can also result if the intermediate is stabilized
Called balanced polymorphism
Balanced Polymorphism & Sickle-cell Anemia

HbA = Normal Allele
HbS = Sickle-cell Anemia







