VPN Overview
(Notes from 'Setting up a VPN' SkillSoft Press © 2002)
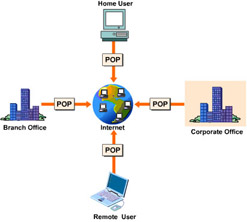
A VPN is a private network that provides a low-cost and secure remote access communication framework. Organizations use it to provide controlled access to the corporate network. A VPN replaces physical dedicated leased line connections with secure virtual connections called tunnels set up over a public network. It provides the benefits of a traditional WAN at a lower cost.
In a VPN, an Internet service provider (ISP) is used to connect to the Internet. To access the local area network (LAN) at the corporate office, a remote user logs on to the local Point of Presence (POP) of an ISP. A POP is an access point to the network of the ISP with an IP address. The ISP provides a local telephone number to log on to the Internet and establish a connection with the corporate LAN. The branch offices and the corporate office are connected to the local POP of the ISP through dedicated leased lines. Mobile users are provided local dial-up access to a POP.
The network of the ISP or the Internet is then used as the backbone to establish a secure VPN connection between the branch office and the corporate office. A VPN implements data security by:
- Authentication: Verifies the identity of the remote user or computer before establishing a VPN connection. Digital certificates and passwords are commonly used authentication methods.
- Encapsulation: Transmits data in the form of Internet Protocol (IP) datagrams. In addition, datagrams other than IP datagrams can be encapsulated within an IP header and transmitted over an IP-based network.
- Encryption: Ensures data security by using encryption keys. The contents of the IP datagram can be deciphered only with the help of the encryption keys. Encryption algorithms, hash functions, and secret keys are used to encrypt and decrypt data.
- Access control: Defines access rights for different users depending on their requirements. Access to the LAN at the corporate office is controlled by classification of remote users into various groups. Each group is assigned different access rights.
Components of a VPN
A VPN uses client-server architecture to provide remote access. A VPN server processes connection requests from remote users. After authentication, they are forwarded to the LAN at the corporate office. The components of a VPN are:
- VPN server: Processes the connection requests made by remote VPN clients. It functions as a gateway device between VPN clients and a private network. Large networks involving multiple requests may need more than one VPN server to prevent network latency. A VPN server has one virtual interface facing the LAN at the corporate office and the other virtual interface towards the Internet. This interface actively receives connection requests.
- VPN client: Sends connection requests to the VPN server. It can be a remote computer or a laptop used by a telecommuter to connect to the local POP of an ISP. It can also be a computer that is a part of the local area network (LAN) at a branch office or the office of a business partner.
- VPN connection: Provides a secure link over the transit internetwork. It is similar to a point-to-point connection between two computers. Data encryption is performed at the two end points of a VPN connection.
- Tunnel: Performs data encapsulation to allow datagrams to be transmitted over an IP-based network, such as the Internet.
- Tunneling protocols: Consist of communication standards that facilitate the creation of secure tunnels over a public network. The commonly used tunneling protocols include Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP), Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP), and Internet Protocol Security (IPSec).
- Tunneled data: Refers to the data packets exchanged between a VPN server and a VPN client through secure tunnels. The data packets are encrypted before transmission by using various encryption algorithms.
- Shared or public network: Represents the transit internetwork in a VPN. It can be a shared or public TCP/IP network, such as the Internet, or an Internet Protocol (IP)-based intranet.
A VPN connection can also be setup between two remote peers located on different network segments.
Advantages of a VPN
Maintaining dedicated leased lines to establish remote access connectivity becomes increasingly expensive as an organization expands. The recurring expenses of long distance calls made by mobile telecommuters increase communication costs. A number of employees prefer to work from home for different reasons. Such employees require access to resources at the corporate office. A VPN meets the remote access requirements of such employees. A VPN provides the following benefits:
- The cost of setting up and maintaining a VPN is lower than the cost of a traditional remote access model. The responsibility of implementing and maintaining the VPN can be passed on to the ISP.
- A VPN allows remote users to easily connect to a corporate LAN across a VPN connection. The large number of POPs allows remote users to dial-up an ISP and set up VPN connections from various locations.
- A VPN provides greater flexibility when compared to a traditional remote access model. It is easier to set up. You can also modify a VPN to incorporate the changing networking requirements of an organization more easily. For example, in a VPN, to connect two new branch offices with the corporate office, you need to install a local telephone connection and a modem to connect to the local POP of an ISP. It is more difficult to set up a remote access connection by using permanent leased lines in the traditional remote access model.
- A number of sophisticated authentication and encryption schemes, such as passwords, digital certificates, and encryption algorithms, are used for securing the data sent over a VPN. You can ensure the security of the private network at the corporate office by allowing remote users to access only specific resources. Different levels of remote access are defined for various remote users.
- A major advantage of using a VPN is the low cost of remote access communication. A VPN not only saves the recurring cost of long distance calls but also saves the cost of dedicated leased lines. In a traditional remote access model, the dedicated leased line covers the entire distance between the branch offices and the corporate office. In contrast, a VPN requires the leased lines only to connect the private network at the corporate office and the branch offices to the local POP of an ISP. In addition, only local call charges are incurred for establishing a VPN connection between mobile users and the corporate intranet.