Comparison of NMR and Molecular Modeling Results for a Rigid
and a Flexible Oligosaccharide
Keywords: oligosaccharide/ conformation/ molecular dynamics
Qiuwei Xu, Rossitza Gitti and C. Allen Bush
Department of Chemistry & Biochemistry,
University of Maryland Baltimore County, Baltimore, MD 21228.
Research supported by NSF Grant MCB 9105586 and by NIH grant GM 31449
Abstract
Three-bond heteronuclear coupling constants (  J
J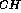 ) are extremely
useful in describing flexible models for oligosaccharides. We show that
antiphase methods for measuring
) are extremely
useful in describing flexible models for oligosaccharides. We show that
antiphase methods for measuring  J
J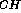 in oligosaccharides have limited
reliability but that the coupling constants can be reliably
measured in natural abundance
by quantitative J-correlation methods. Interpretation of
in oligosaccharides have limited
reliability but that the coupling constants can be reliably
measured in natural abundance
by quantitative J-correlation methods. Interpretation of  J
J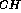 data for a pentasaccharide (lacto-N-fucopentaose 2)
from human milk are consistent with a rigid model for the Lewis
data for a pentasaccharide (lacto-N-fucopentaose 2)
from human milk are consistent with a rigid model for the Lewis trisaccharide epitope but for an antigenic tetrasaccharide
fragment from the cell wall polysaccharide of viridans streptococci,
trisaccharide epitope but for an antigenic tetrasaccharide
fragment from the cell wall polysaccharide of viridans streptococci,
 J
J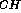 data imply a
considerably more flexible model. Nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE)
data are reported for a heptasaccharide repeating unit isolated from the
cell wall polysaccharide of
Streptococcus gordonii 38. The results for a tetrasaccharide
fragment are similar to data reported
for the same fragment in the cell wall polysaccharide
from S. mitis J22. This result implies a similar conformation
for the tetrasaccharide fragment in the polysaccharide and in
the heptasaccharide and also implies that anisotropy of motion is not
significant in the interpretation of the nuclear Overhauser effects in
the polysaccharide. Interpretation of the NOE results for the tetrasaccharide
fragment, like the
data imply a
considerably more flexible model. Nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE)
data are reported for a heptasaccharide repeating unit isolated from the
cell wall polysaccharide of
Streptococcus gordonii 38. The results for a tetrasaccharide
fragment are similar to data reported
for the same fragment in the cell wall polysaccharide
from S. mitis J22. This result implies a similar conformation
for the tetrasaccharide fragment in the polysaccharide and in
the heptasaccharide and also implies that anisotropy of motion is not
significant in the interpretation of the nuclear Overhauser effects in
the polysaccharide. Interpretation of the NOE results for the tetrasaccharide
fragment, like the  J
J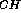 data, implies a flexible model with three
conformations in fast exchange. The results of the
two experimental techniques are combined with molecular modeling results
including molecular dynamics simulation to provide a clear delineation
between flexible and rigid oligosaccharide epitopes.
The blood group Lewis
data, implies a flexible model with three
conformations in fast exchange. The results of the
two experimental techniques are combined with molecular modeling results
including molecular dynamics simulation to provide a clear delineation
between flexible and rigid oligosaccharide epitopes.
The blood group Lewis trisaccharide antigenic determinant
is highly restricted in its motions
by steric interactions while the antigenic tetrasaccharide
fragment of the S. gordonii 38 heptasaccharide is
considerably more mobile. We propose that some branched
oligosaccharides are relatively
rigid and some are flexible depending on subtle details
of the linkages.
trisaccharide antigenic determinant
is highly restricted in its motions
by steric interactions while the antigenic tetrasaccharide
fragment of the S. gordonii 38 heptasaccharide is
considerably more mobile. We propose that some branched
oligosaccharides are relatively
rigid and some are flexible depending on subtle details
of the linkages.
Dr. Allen Bush; CHEM
Wed Nov 13 16:21:50 EST 1996
 J
J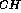 ) are extremely
useful in describing flexible models for oligosaccharides. We show that
antiphase methods for measuring
) are extremely
useful in describing flexible models for oligosaccharides. We show that
antiphase methods for measuring  J
J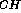 in oligosaccharides have limited
reliability but that the coupling constants can be reliably
measured in natural abundance
by quantitative J-correlation methods. Interpretation of
in oligosaccharides have limited
reliability but that the coupling constants can be reliably
measured in natural abundance
by quantitative J-correlation methods. Interpretation of  J
J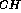 data for a pentasaccharide (lacto-N-fucopentaose 2)
from human milk are consistent with a rigid model for the Lewis
data for a pentasaccharide (lacto-N-fucopentaose 2)
from human milk are consistent with a rigid model for the Lewis trisaccharide epitope but for an antigenic tetrasaccharide
fragment from the cell wall polysaccharide of viridans streptococci,
trisaccharide epitope but for an antigenic tetrasaccharide
fragment from the cell wall polysaccharide of viridans streptococci,
 J
J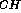 data imply a
considerably more flexible model. Nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE)
data are reported for a heptasaccharide repeating unit isolated from the
cell wall polysaccharide of
Streptococcus gordonii 38. The results for a tetrasaccharide
fragment are similar to data reported
for the same fragment in the cell wall polysaccharide
from S. mitis J22. This result implies a similar conformation
for the tetrasaccharide fragment in the polysaccharide and in
the heptasaccharide and also implies that anisotropy of motion is not
significant in the interpretation of the nuclear Overhauser effects in
the polysaccharide. Interpretation of the NOE results for the tetrasaccharide
fragment, like the
data imply a
considerably more flexible model. Nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE)
data are reported for a heptasaccharide repeating unit isolated from the
cell wall polysaccharide of
Streptococcus gordonii 38. The results for a tetrasaccharide
fragment are similar to data reported
for the same fragment in the cell wall polysaccharide
from S. mitis J22. This result implies a similar conformation
for the tetrasaccharide fragment in the polysaccharide and in
the heptasaccharide and also implies that anisotropy of motion is not
significant in the interpretation of the nuclear Overhauser effects in
the polysaccharide. Interpretation of the NOE results for the tetrasaccharide
fragment, like the  J
J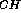 data, implies a flexible model with three
conformations in fast exchange. The results of the
two experimental techniques are combined with molecular modeling results
including molecular dynamics simulation to provide a clear delineation
between flexible and rigid oligosaccharide epitopes.
The blood group Lewis
data, implies a flexible model with three
conformations in fast exchange. The results of the
two experimental techniques are combined with molecular modeling results
including molecular dynamics simulation to provide a clear delineation
between flexible and rigid oligosaccharide epitopes.
The blood group Lewis trisaccharide antigenic determinant
is highly restricted in its motions
by steric interactions while the antigenic tetrasaccharide
fragment of the S. gordonii 38 heptasaccharide is
considerably more mobile. We propose that some branched
oligosaccharides are relatively
rigid and some are flexible depending on subtle details
of the linkages.
trisaccharide antigenic determinant
is highly restricted in its motions
by steric interactions while the antigenic tetrasaccharide
fragment of the S. gordonii 38 heptasaccharide is
considerably more mobile. We propose that some branched
oligosaccharides are relatively
rigid and some are flexible depending on subtle details
of the linkages.